Summary
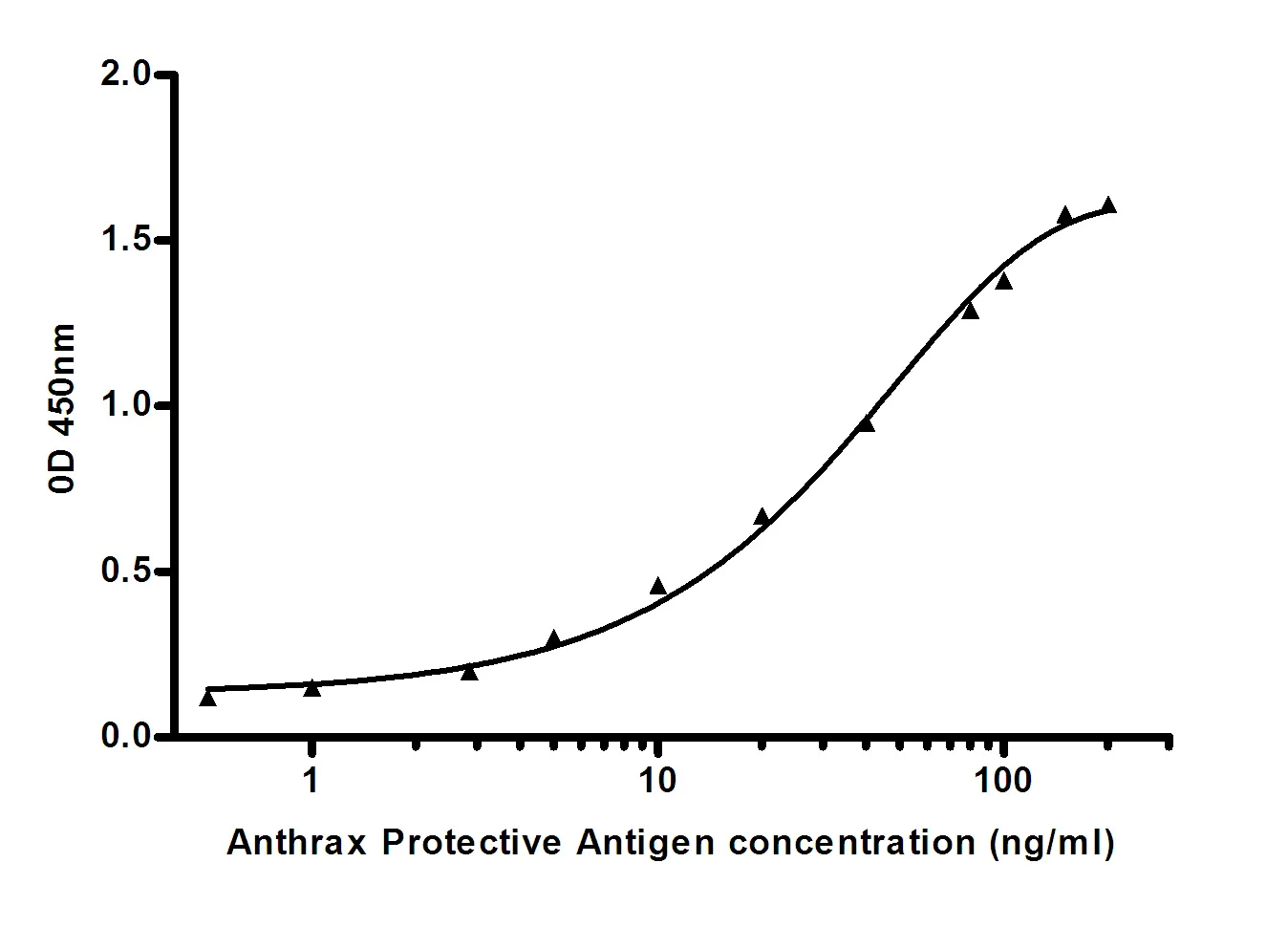
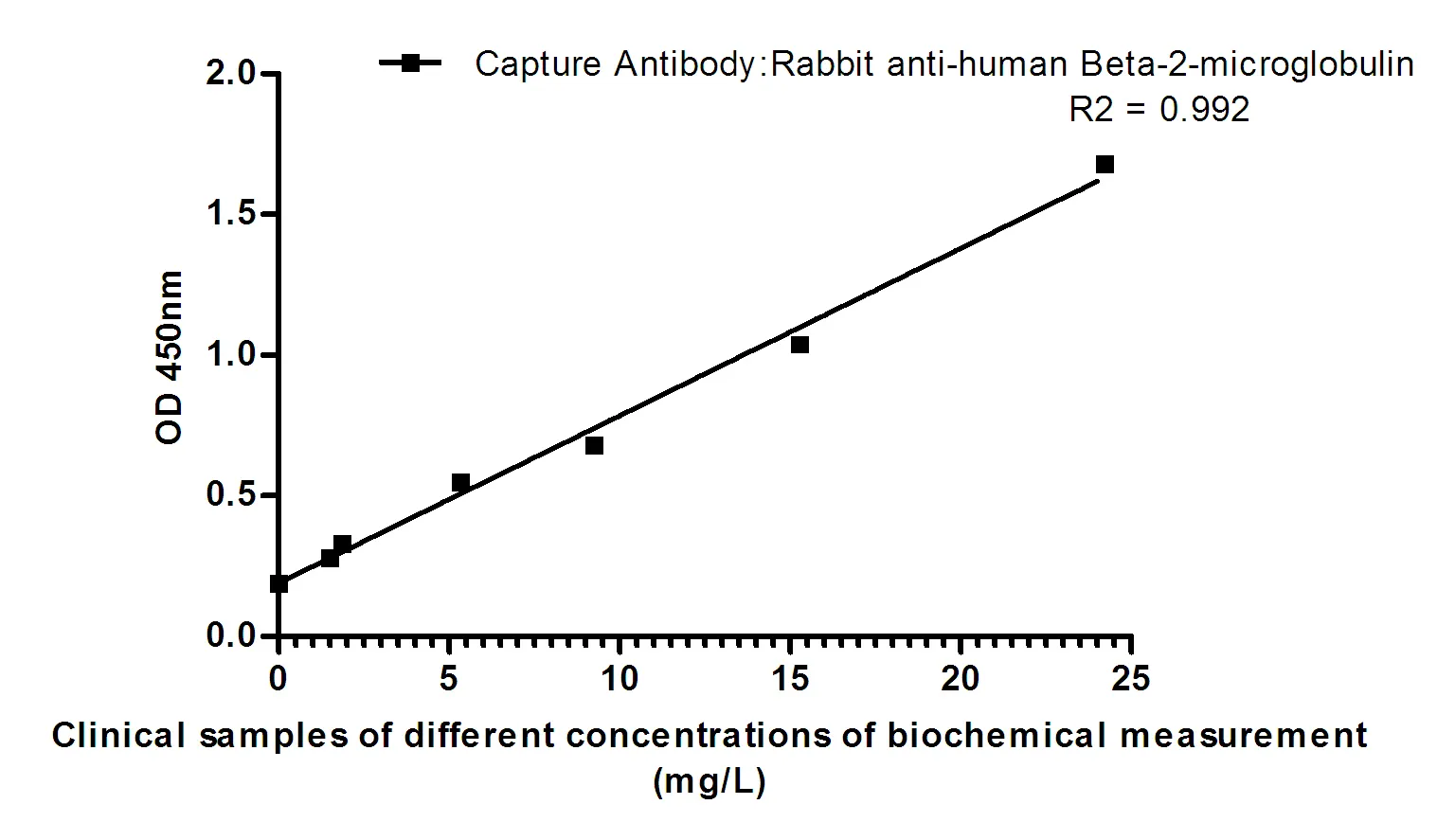
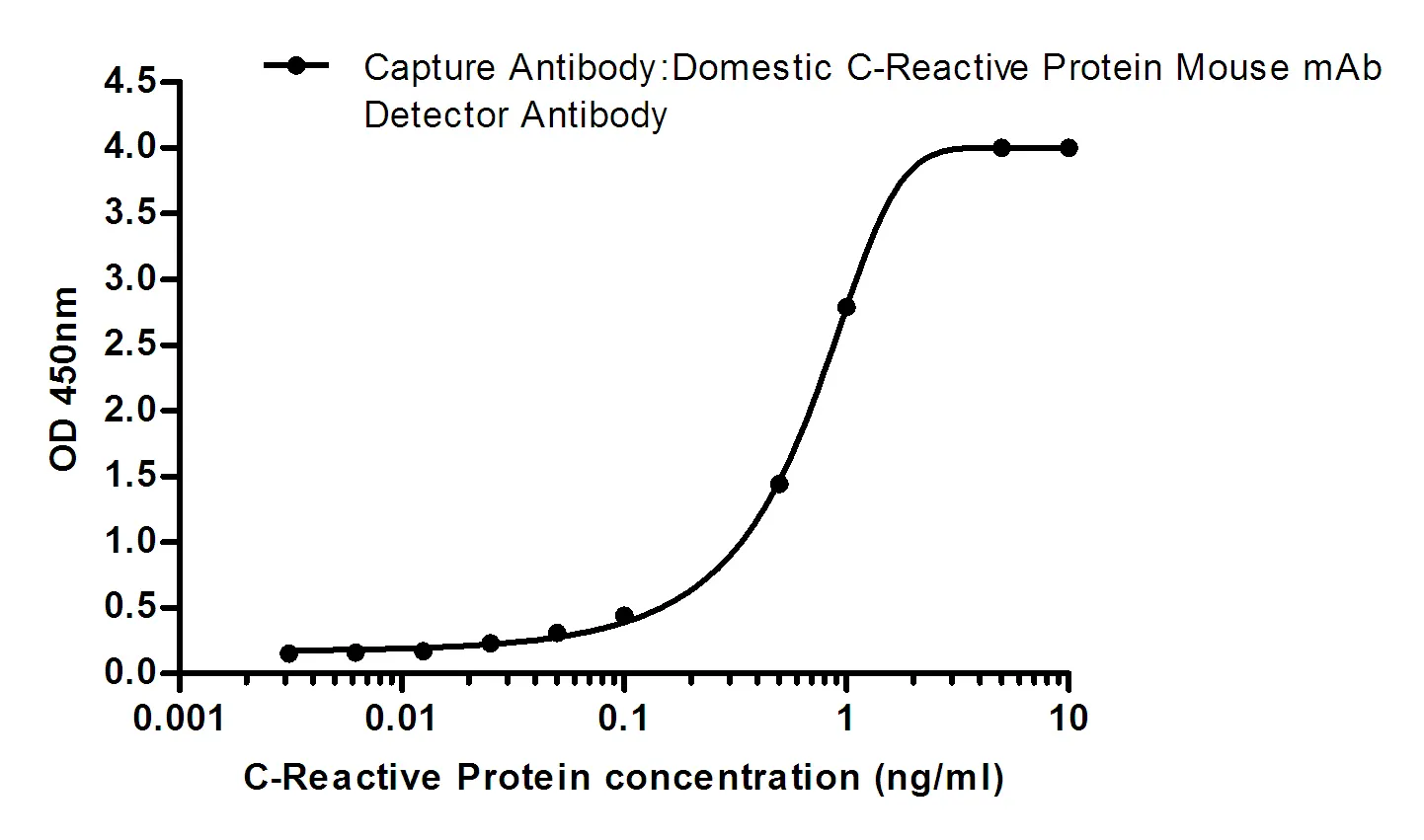
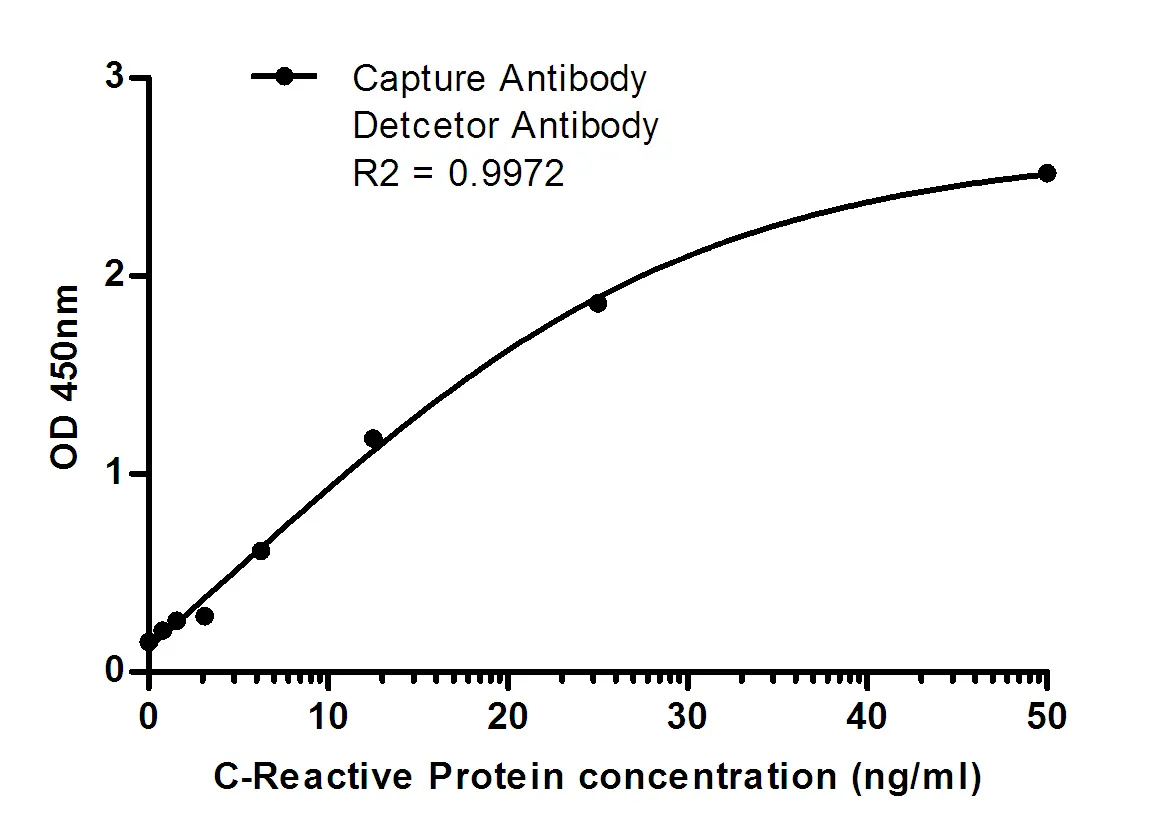
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Cleaves P(1)-P(3)-bis(5'-adenosyl) triphosphate (Ap3A) to yield AMP and ADP. Can also hydrolyze P(1)-P(4)-bis(5'- adenosyl) tetraphosphate (Ap4A), but has extremely low activity with ATP. Modulates transcriptional activation by CTNNB1 and thereby contributes to regulate the expression of genes essential for cell proliferation and survival, such as CCND1 and BIRC5. Plays a role in the induction of apoptosis via SRC and AKT1 signaling pathways. Inhibits MDM2-mediated proteasomal degradation of p53/TP53 and thereby plays a role in p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis. Induction of apoptosis depends on the ability of FHIT to bind P(1)-P(3)-bis(5'-adenosyl) triphosphate or related compounds, but does not require its catalytic activity, it may in part come from the mitochondrial form, which sensitizes the low- affinity Ca(2+) transporters, enhancing mitochondrial calcium uptake. Functions as tumor suppressor.
Research Area
Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling