Product Overview
The EnkiLife Biotin Labeling Kit offers a selection of biotin types commonly used in laboratories. Each kit includes all necessary reagents for labeling, designed specifically for proteins and antibodies with primary amino groups. The components of this kit are intended for labeling antibodies or proteins of comparable size to antibodies, by default.
Product Features
- Fast: Labeling reaction takes only about 30 minutes, balancing both labeling efficiency and effectiveness.
- Rich in variety: We provide a variety of biotin types to meet various application requirements.
- Outstanding effect: targeted optimization of labeling buffer, labeling site is far away from antigen binding site, and labeled antibody has high homogeneity.
- Convenient: Each biotin reagent has been optimized and designed with the corresponding antibody amount, and has been activated and can be used directly, without the need for tedious calculations. The batches are stable and the best results can be achieved by following the steps.
Biotin Introduction
Biotin, also known as vitamin H, coenzyme R, and vitamin B7, is a water-soluble substance. Its molecular core structure is composed of a urea-based ring and a tetrahydrothiophene ring. The interaction between biotin and avidin (avidin or streptavidin) is a useful tool in non-radioactive purification, detection, immobilization, labeling, viral vector targeting and drug targeting systems. The superaffinity between biotin and avidin is one of the strongest non-covalent interactions known between proteins and ligands, and the two bind very quickly and once formed, they are not affected by pH, temperature, organic solvents and other denaturing agents.
In addition to having a strong affinity with avidin, biotin also has two characteristics, making it an ideal molecule for labeling proteins and macromolecules. First, biotin is relatively small than globular proteins, thus minimizing significant interference to many proteins and allowing multiple biotin molecules to bind to a single protein, thus maximizing detection capabilities. Depending on the use scenarios, more and more different types of biotin and their derivatives have been developed, such as containing different activation groups, different solubility, different spacer lengths, and different biotin derivatives such as biocytin and desulfurization biotin, which greatly expands the application scope of biotin.
In many protein research applications, biotin-labeled proteins are often detected or purified using avidin conjugates, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), western blot analysis, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunoprecipitation (IP) and other affinity purification methods, cell surface labeling and flow cytometry (FC)/cell sorting (FACS).
| Biotin Type | Spacer arm length | Solubility | Key Features | Catalog Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfo-NHS-Biotin | 13.5 Å | Water Solubility | Membrane impermeable, short arms, sulfonic acid group, high solubility in aqueous solution | RE80002q |
| Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin | 22.4 Å | Water Solubility | Membrane impermeable, medium arm length, sulfonic acid group, high solubility in aqueous solution | RE80002s |
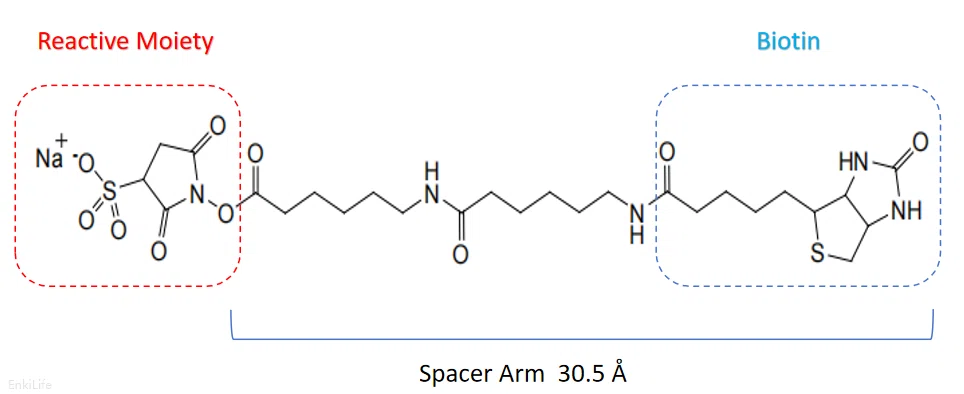
| Sulfo-NHS-LC-LC-Biotin | 30.5 Å | Water Solubility | Membrane impermeable, enhanced arm length, sulfonic acid group, high solubility in aqueous solution | RE80002u |
| Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin | 24.3 Å | Water Solubility | Membrane impermeable, selective cutting possible | RE80002v |
| NHS-PEG4-Biotin | 29.0 Å | Water Solubility | PEGylation to prevent protein aggregation | RE80002w |
- When the molecular weight of the final labeled product needs to be as small as possible, choose the Short-Arm Biotin Labeling Kit.
- When follow-up applications require the use of reducing agents to cleave the biotin tag, choose the Sulfo-NHS-SS-Biotin Labeling Kit.
- When you need to maximize protein solubility and prevent protein aggregation, choose the NHS-PEG4-Biotin labeling kit.
- When you want the final binding steric hindrance to be smaller, choose the long-arm biotin labeling kit and select the appropriate arm length based on the binding characteristics.
Kit Specifications
| Product Components | Component Content in Different Specifications | Storage Temperature | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40μg Antibody | 200μg Antibody | 2mg Antibody | ||
| Activated Biotin | 1 tube | 5 tubes | 5 tubes | -20°C after opening, protected from light |
| 50KDa Ultrafiltration Tube* | 1 set** | 1 set** | 1 set** | RT |
| Labeling Buffer B | 10 mL | 10 mL | 10 mL | 2~8°C |
| 1×PBS (pH 7.4) | 10 mL | 10 mL | 10 mL | 2~8°C |
| DMF | 100 μL | 100 μL | 100 μL | 2~8°C, protected from light |
| Labeled Protein Storage Solution | 200 μL | 1 mL | 5 mL | 2~8°C |
| Recommended Labeling Amount | Each tube dyes for labeling 20-40μg antibody Recommended: 20μg antibody | Each tube dyes for labeling 20-40μg antibody Recommended: 20μg antibody | Each tube dyes for labeling 100-400μg antibody Recommended: 200μg antibody | |
* Ultrafiltration tube molecular weight cutoff: 50KDa
** 1 set = 1 ultrafiltration tube and collection tube
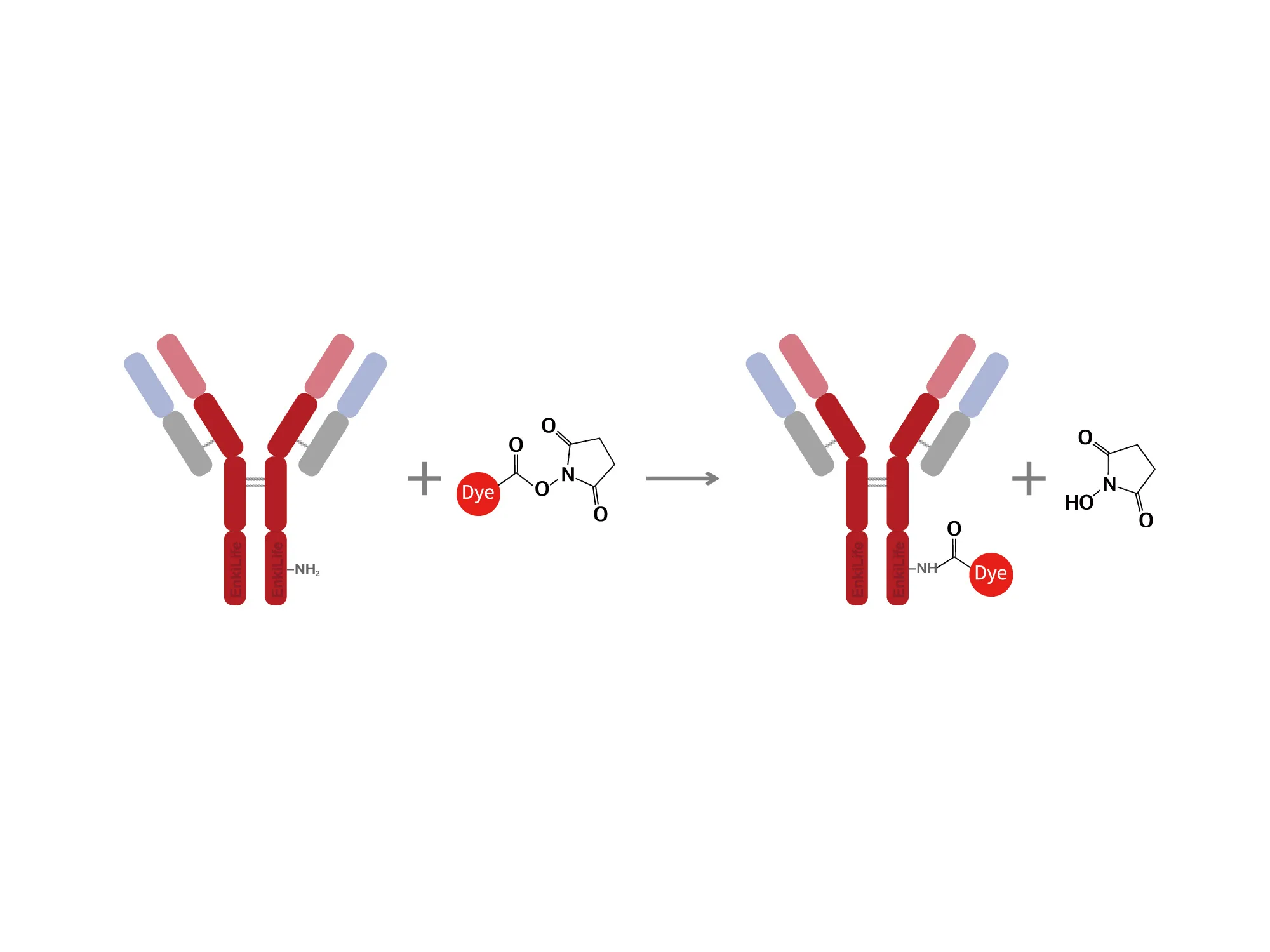
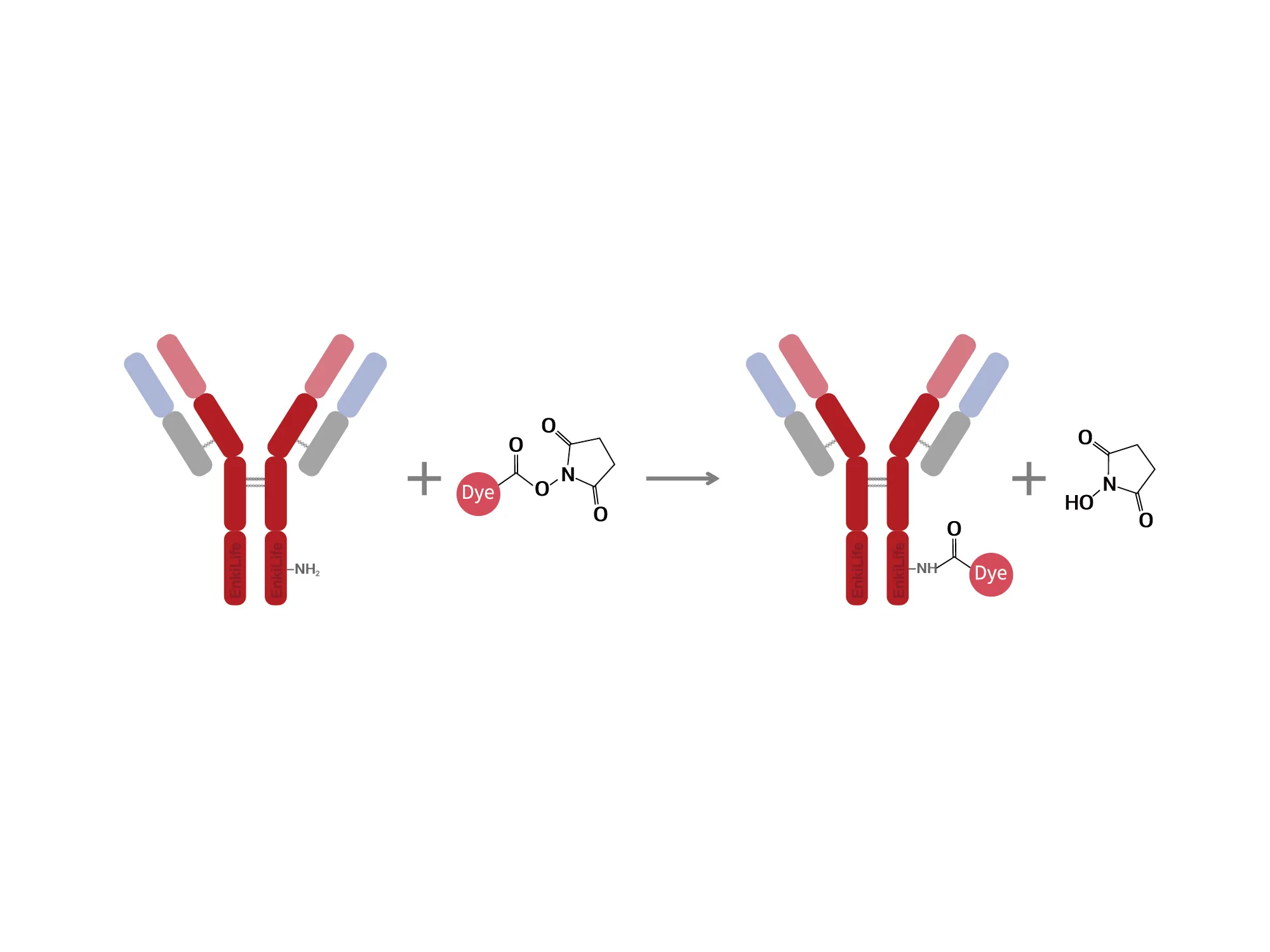
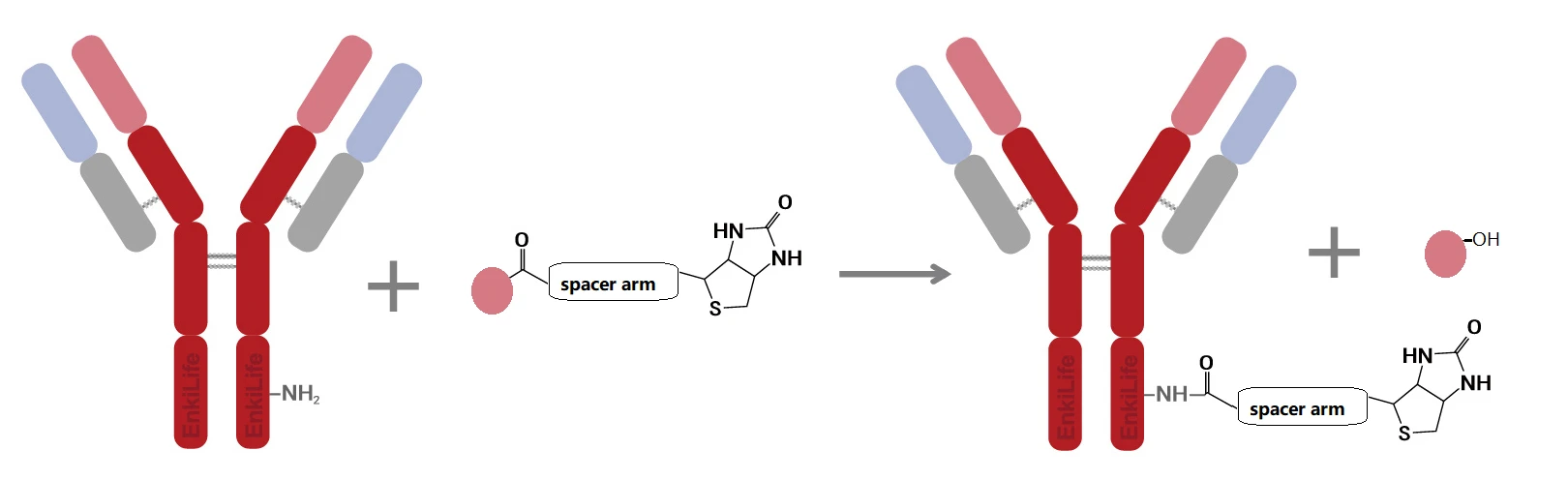
Labeling Principle
Within a certain pH range, biotin reacts specifically with primary amino groups to form stable amide bonds, thereby achieving coupling with proteins.
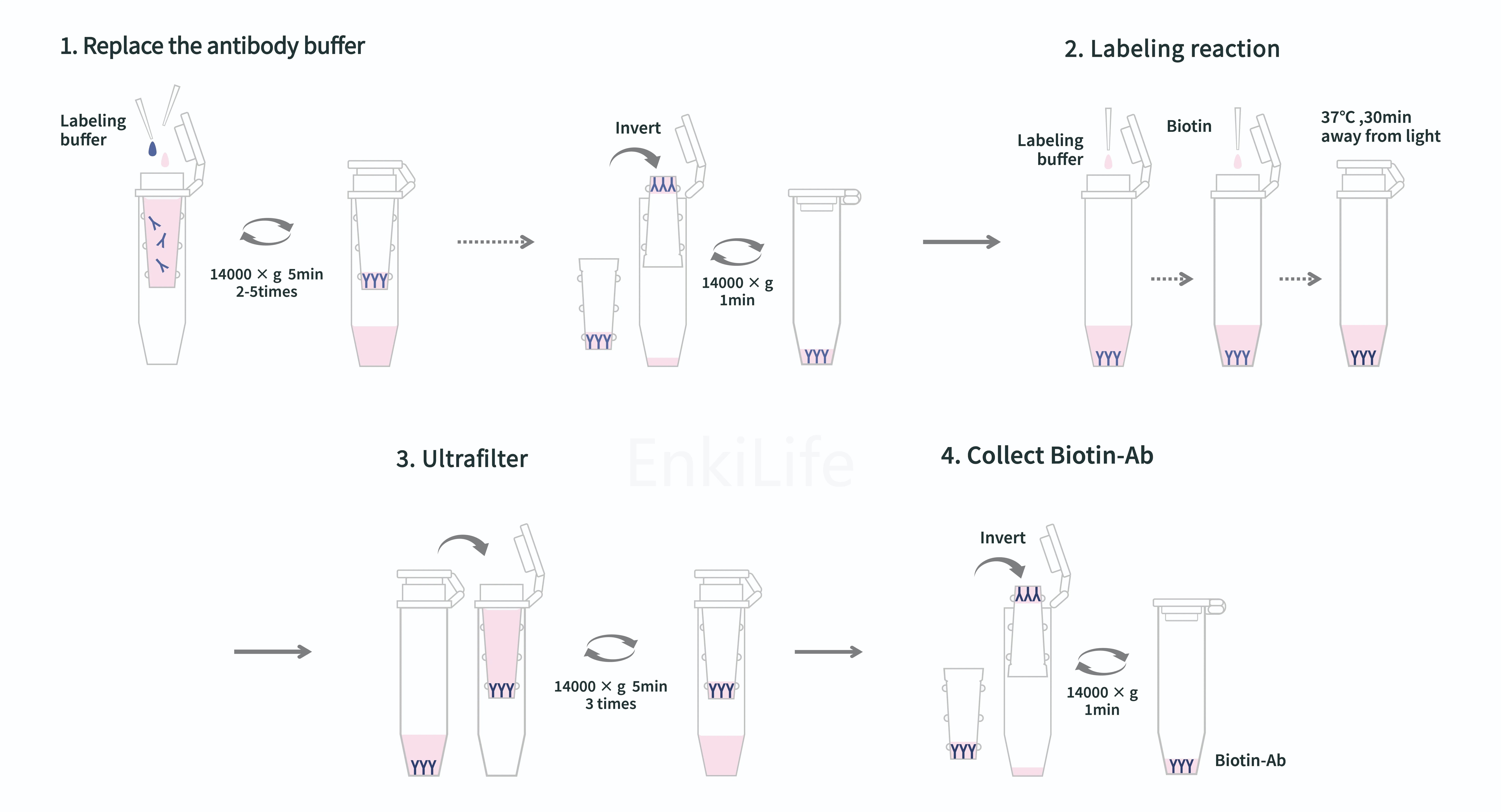
Standard Labeling Procedure
- 1.Ultrafiltration for buffer exchange and concentration
- 2.Labeling reaction
- 3.Purification
- 4.Storage