Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGFs)
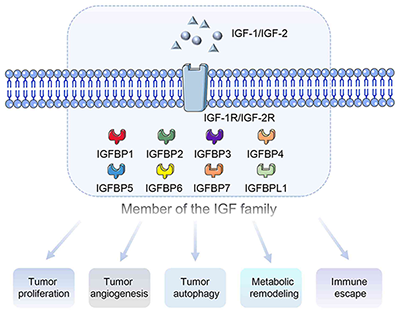
The IGF family consists mainly of two low-molecular-weight protein (IGF-1 and IGF-2), the corresponding receptors (IGF-1R and IGF-2R) and specific binding proteins. In 1963, Froesch et al discovered the presence of a certain active substance in serum that could not be completely inhibited by insulin antibodies; this substance was subsequently purified by two scientists, Rinderknecht and Humbel, and named IGF-1 and IGF-2. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) and insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) can bind to their receptor, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R), and subsequently trigger downstream cascades by phosphorylating insulin receptor substrates and binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and growth factor receptor-bound protein 2-associated protein (Grb2), thereby activating two important signaling pathways: (1) The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which mainly induces various responses in transcription and metabolism, and regulates cell growth, survival, and differentiation. (2) The PI3K pathway, which is involved in cell survival, growth, and proliferation, as well as protein synthesis.
Product List
| Target | Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Predicted MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
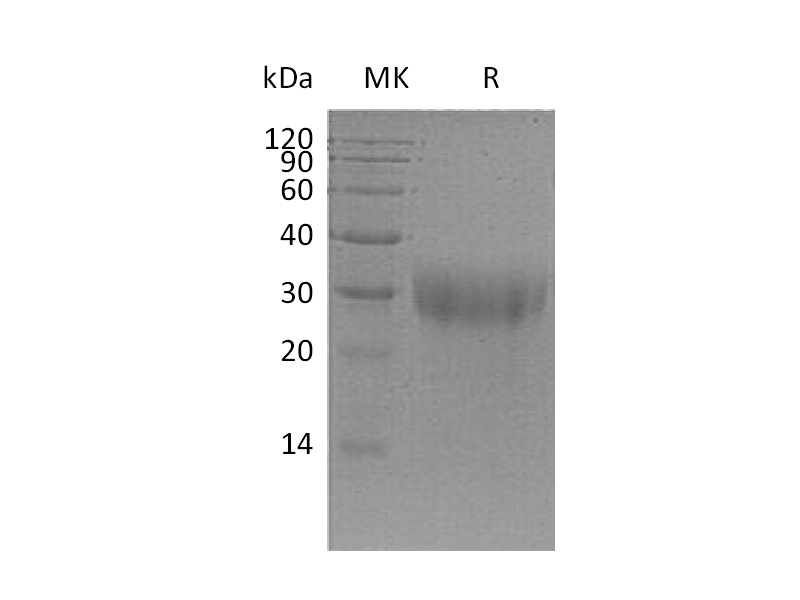
PLGF (C-6His) | PHM1319 | Recombinant Mouse PLGF (C-6His) | Mouse | 16.9 kDa |
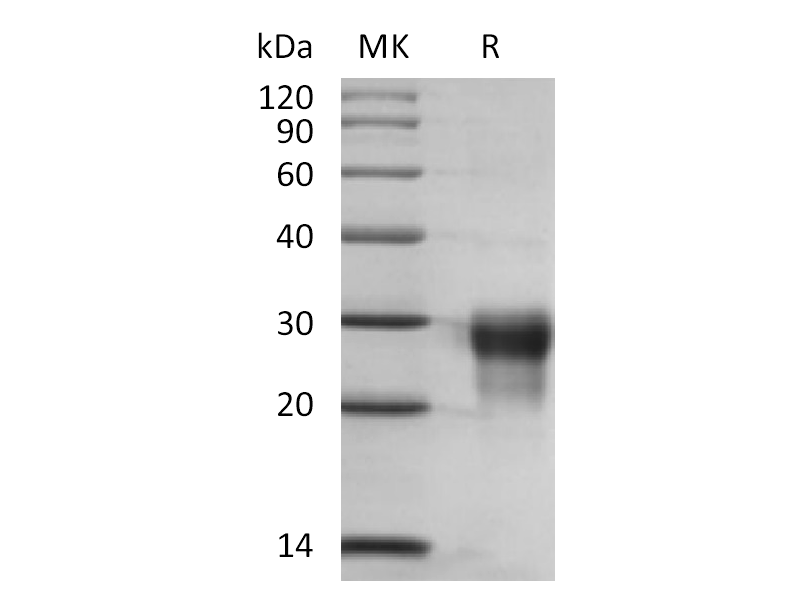
PLGF-2 (C-6His) | PHH2178 | Recombinant Human PLGF-2 (C-6His) | Human | 18.2 kDa |
Validation Data
Recombinant Mouse PLGF (C-6His) (Catalog: PHM1319) Recombinant Human PLGF-2 (C-6His) (Catalog: PHH2178)
Related Products
Super-sensitive ECL chemiluminescent reagent
References
1. Insulin-like growth factors. LeRoith D, et al. Biol Signals. 1992. [PMID: 1307923]
2. Insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and fetal growth and skeletal development (Review). Agrogiannis GD, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2014. [PMID: 24859417]
3. Insulin-like growth factor in cancer: New perspectives (Review). Wu D, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2025. [PMID: 40417926]
4. Molecular and cellular aspects of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. LeRoith D, et al. Endocr Rev. 16:143–163. 1995.
5. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Jones JI, et al. Endocr Rev. 1995. [PMID: 7758431]
6. Insulin-like Growth Factors and Dermatosis. Tang HY, et al. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2019. [PMID: 31282339]
7. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. Rinderknecht E, et al. J Biol Chem. 1978 . [PMID: 632300]
8. Antibody-suppressible and nonsuppressible insulin-like activities in human serum and their physiologic significance. An insulin assay with adipose tissue of increased precision and specificity. Froesch ER, et al. J Clin Invest. 1963. [PMID: 14083170]
