Summary
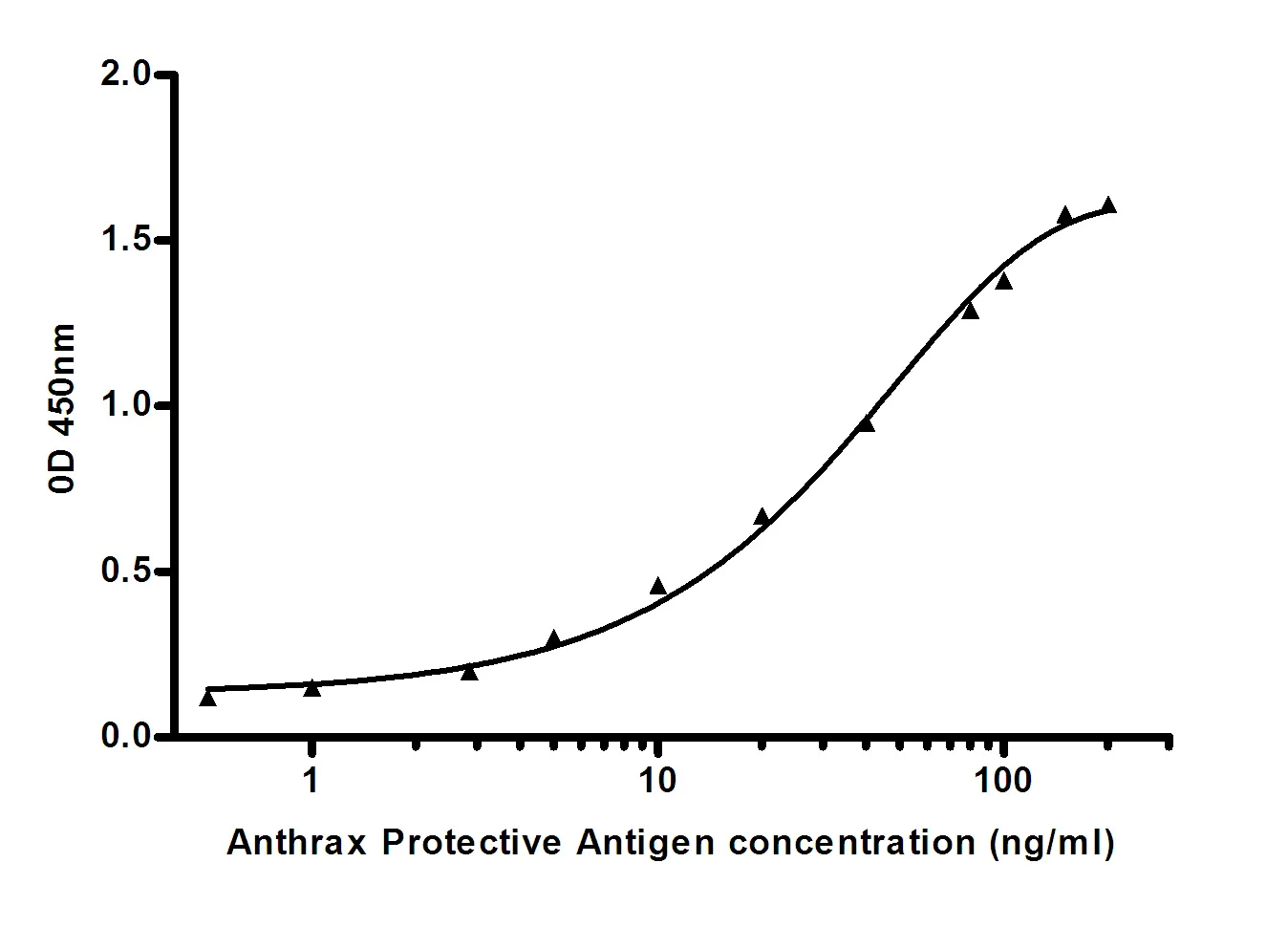
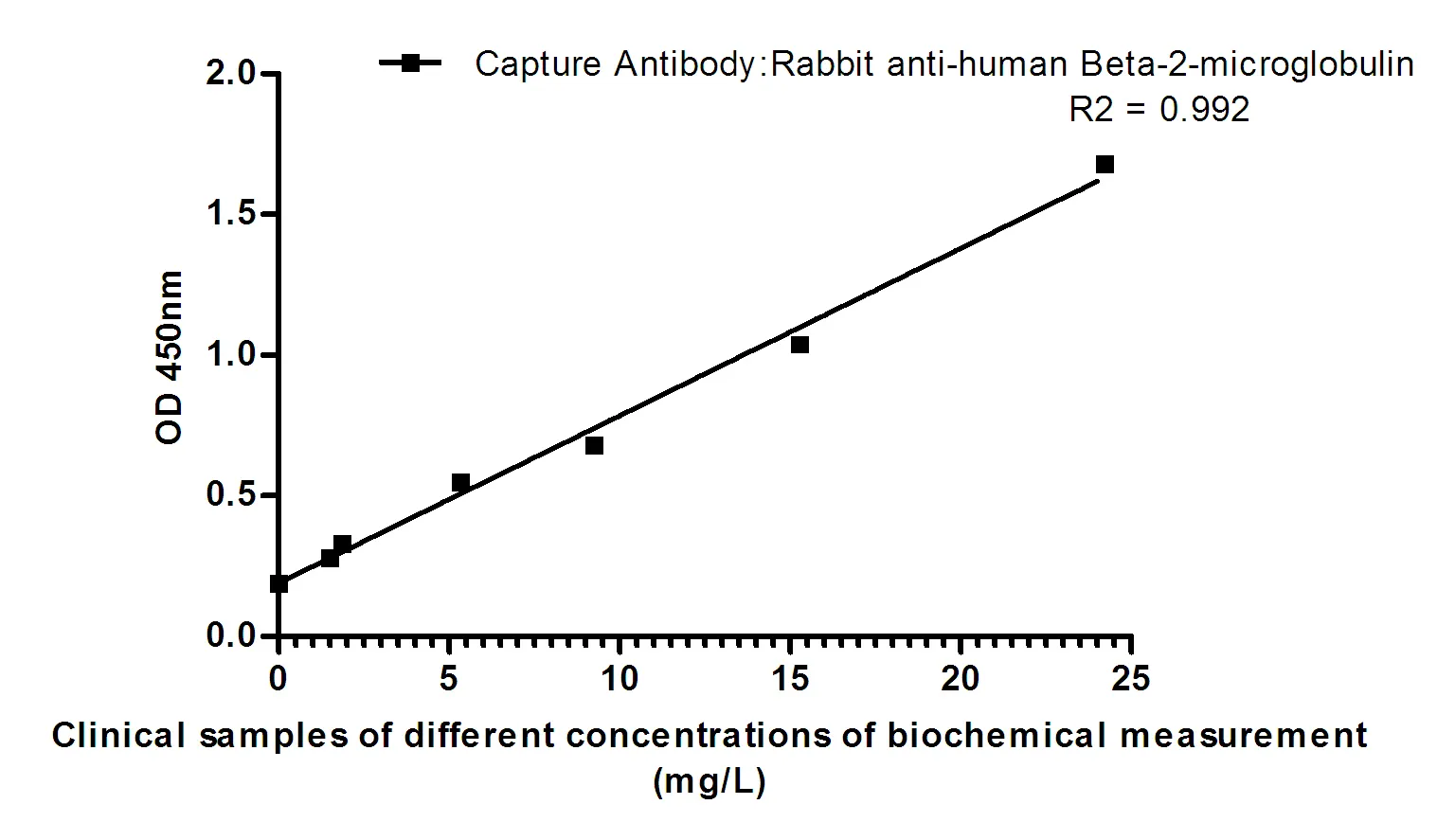
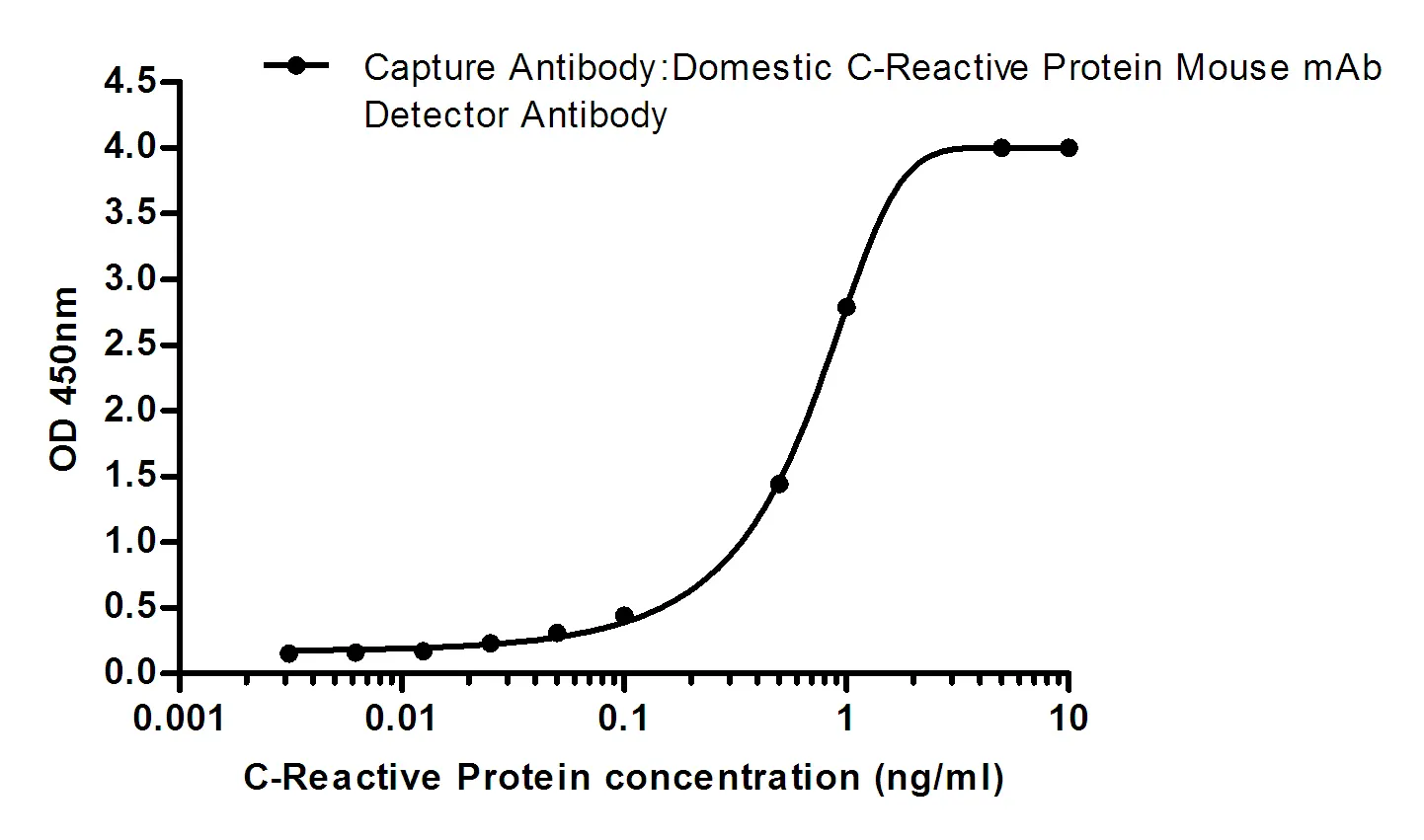
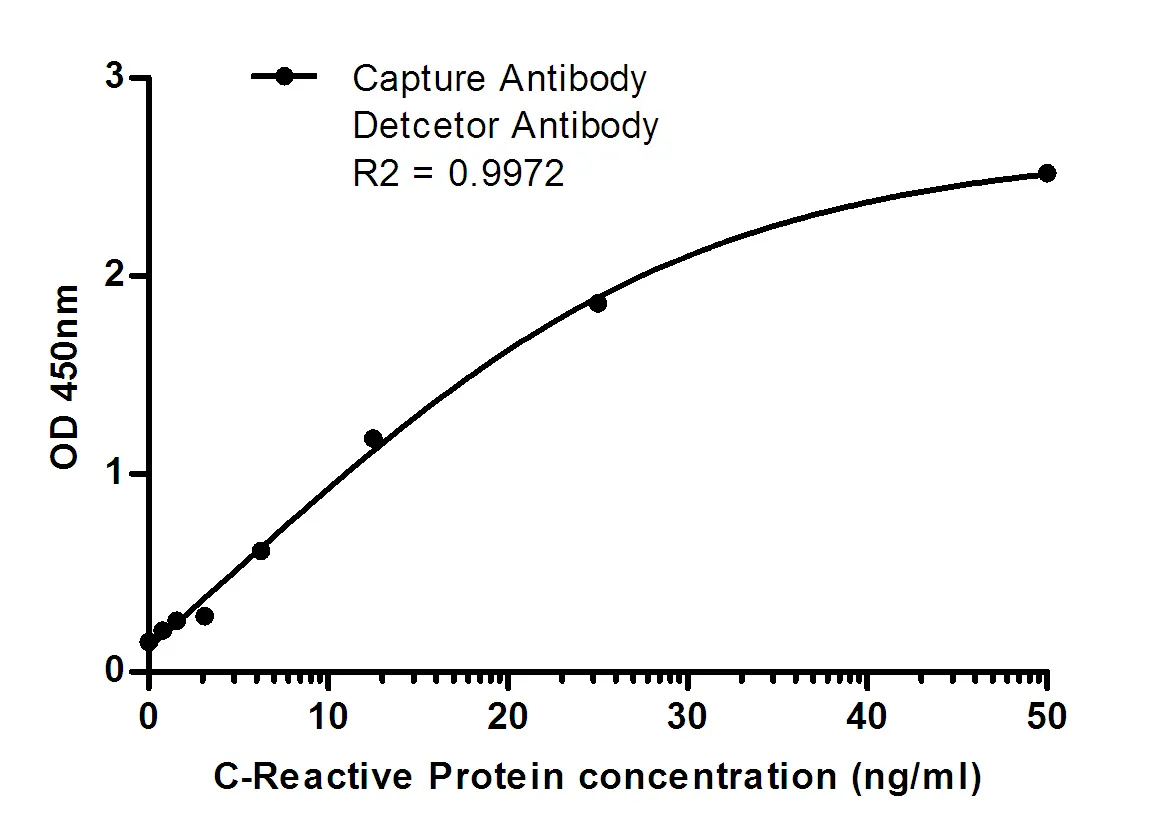
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Subunit of mTORC1, which regulates cell growth and survival in response to nutrient and hormonal signals. mTORC1 is activated in response to growth factors or amino acids. Growth factor-stimulated mTORC1 activation involves a AKT1-mediated phosphorylation of TSC1-TSC2, which leads to the activation of the RHEB GTPase that potently activates the protein kinase activity of mTORC1. Amino acid-signaling to mTORC1 requires its relocalization to the lysosomes mediated by the Ragulator complex and the Rag GTPases. Activated mTORC1 up-regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylating key regulators of mRNA translation and ribosome synthesis. mTORC1 phosphorylates EIF4EBP1 and releases it from inhibiting the elongation initiation factor 4E (eiF4E). mTORC1 phosphorylates and activates S6K1 at 'Thr-389', which then promotes protein synthesis by phosphorylating PDCD4 and targeting it for degradation. Within mTORC1, AKT1S1 negatively regulates mTOR activity in a manner that is dependent on its phosphorylation state and binding to 14-3-3 proteins. Inhibits RHEB-GTP-dependent mTORC1 activation. Substrate for AKT1 phosphorylation, but can also be activated by AKT1-independent mechanisms. May also play a role in nerve growth factor-mediated neuroprotection.
Research Area
Cell Biology