Summary
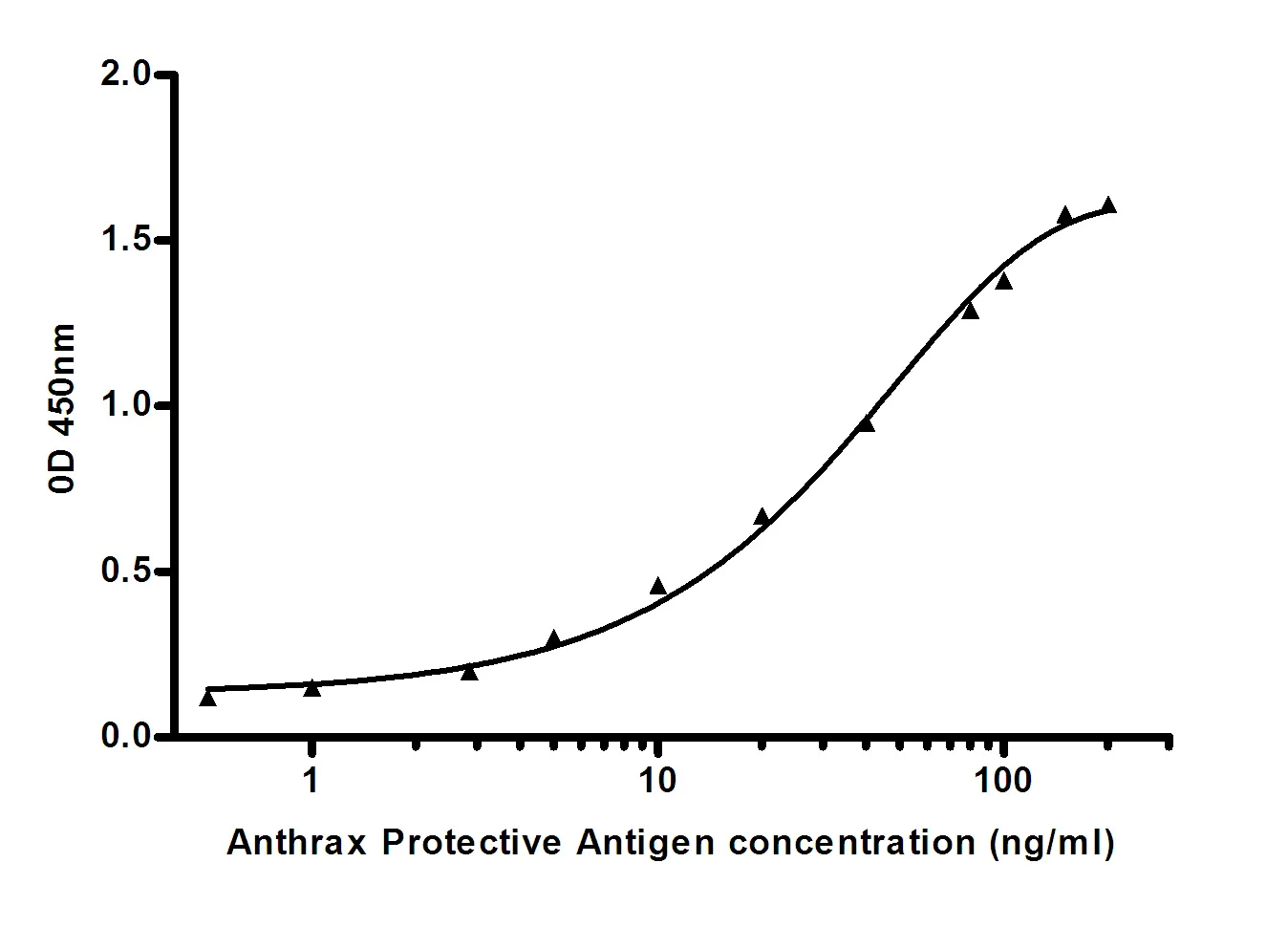
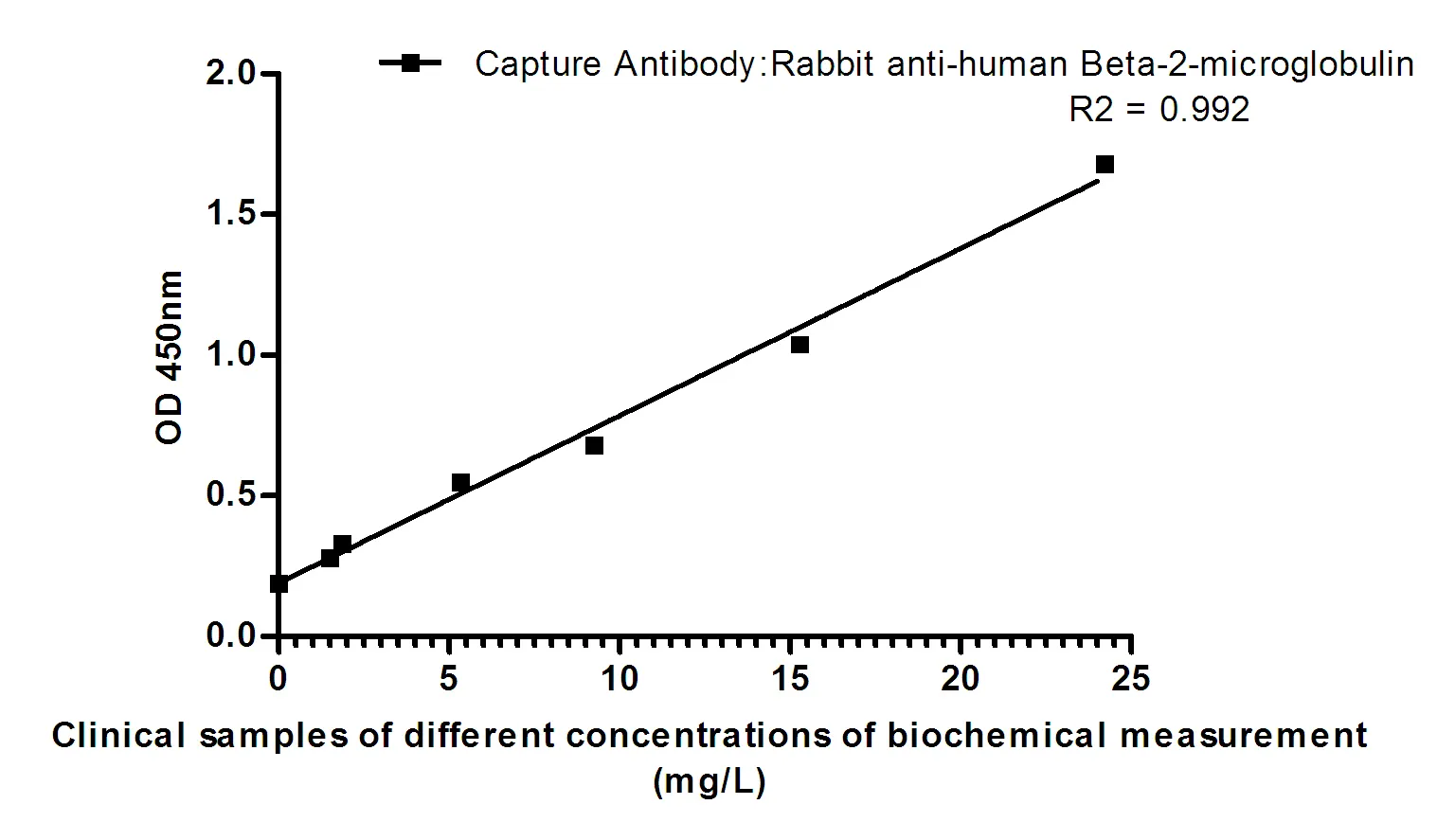
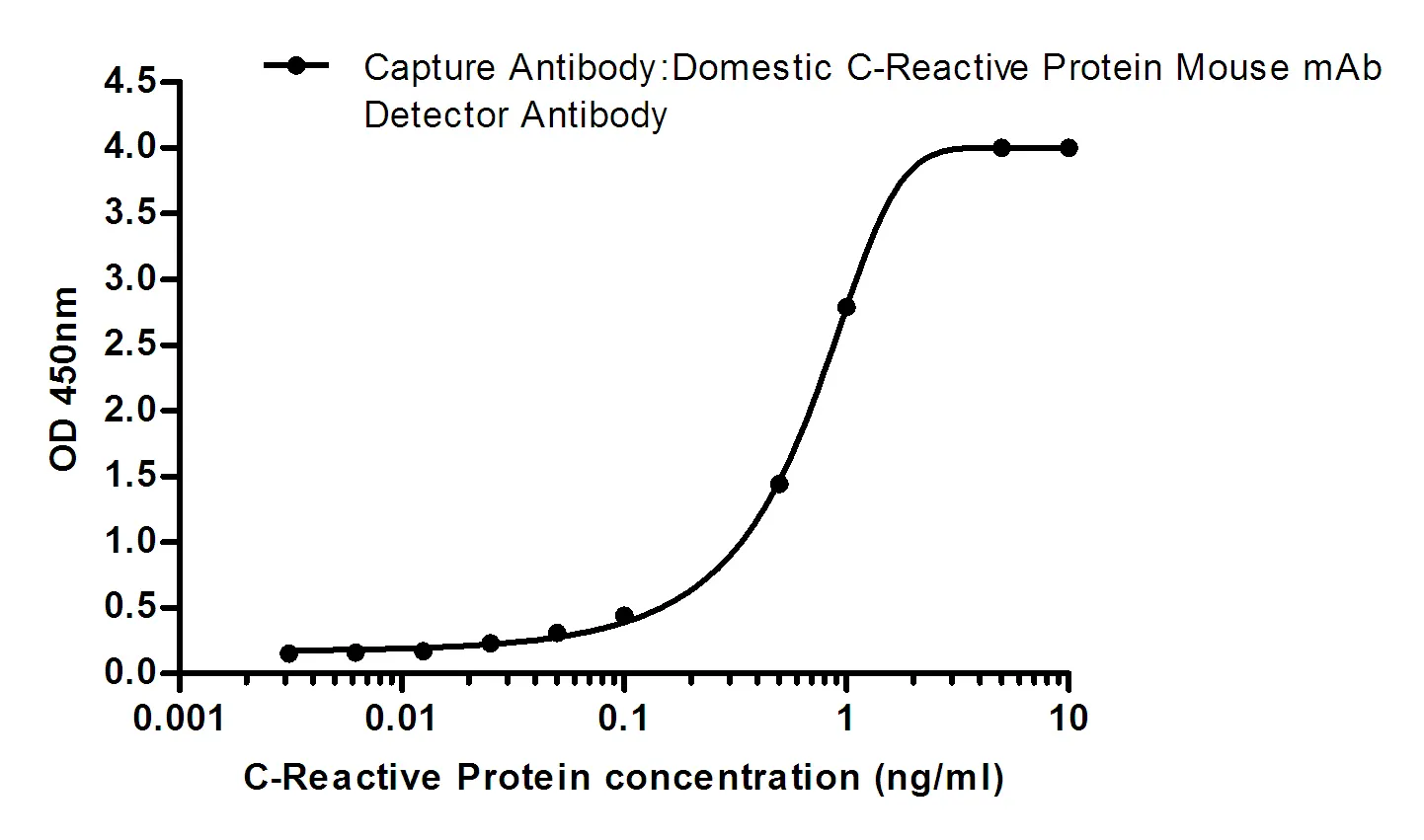
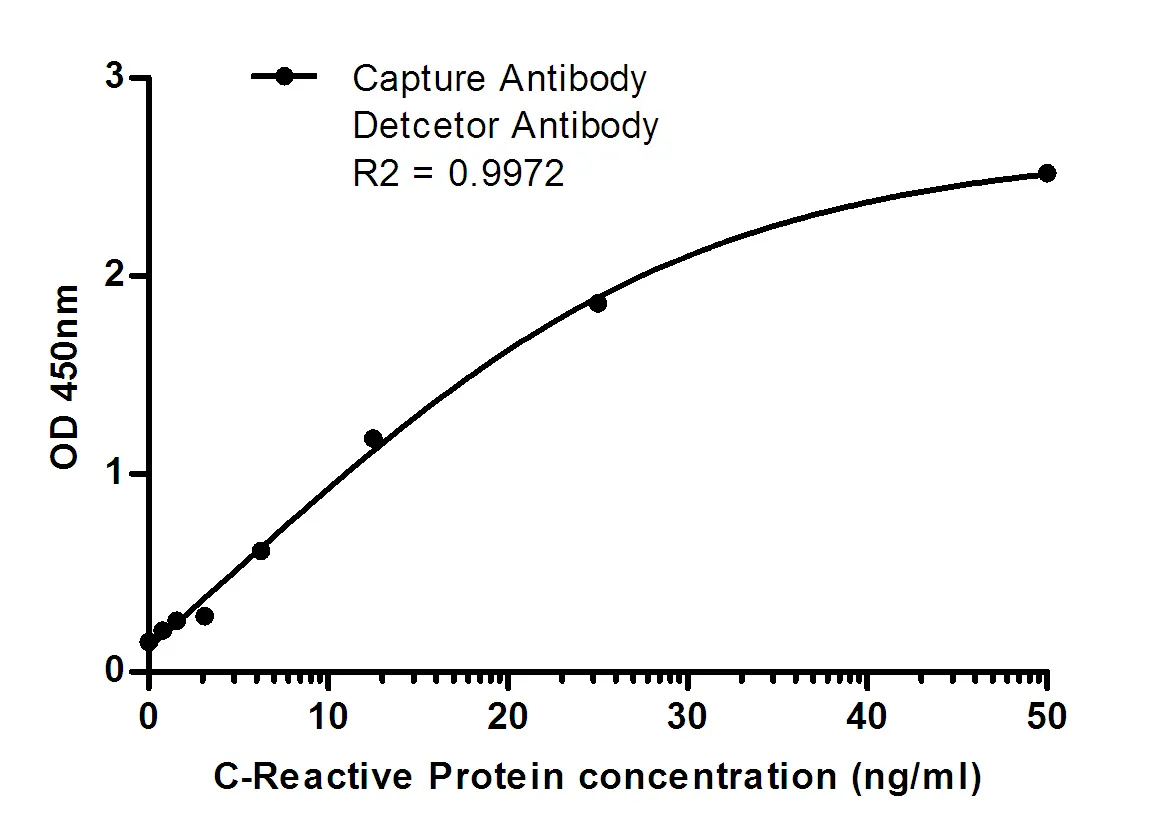
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
This gene encodes a strongly conserved protein that has an N-terminal coiled-coil domain followed by an armadillo domain, five 20-amino acid repeats, and two SAMP domains. This protein promotes the assembly of a multiprotein complex that recruits and phosphorylates the Wnt effector beta-catenin and targets beta-catenin for ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation. This protein therefore plays a role in the reduction of cytoplasmic levels of beta-catenin which in turn reduces activation of Wnt target genes that play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of various human cancers. The protein encoded by this gene is closely related to the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor-suppressor protein and has similar tumor-suppressor effects. This gene also plays a role in actin assembly, cell-cell adhesion, and microtubule network formation through its interaction with cytoskeletal proteins. This gene has its highest expression in the central nervous system and is involved in brain development through cytoskeletal regulation in neurons. Alternative splicing produces multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.
Research Area
Wnt signaling pathway