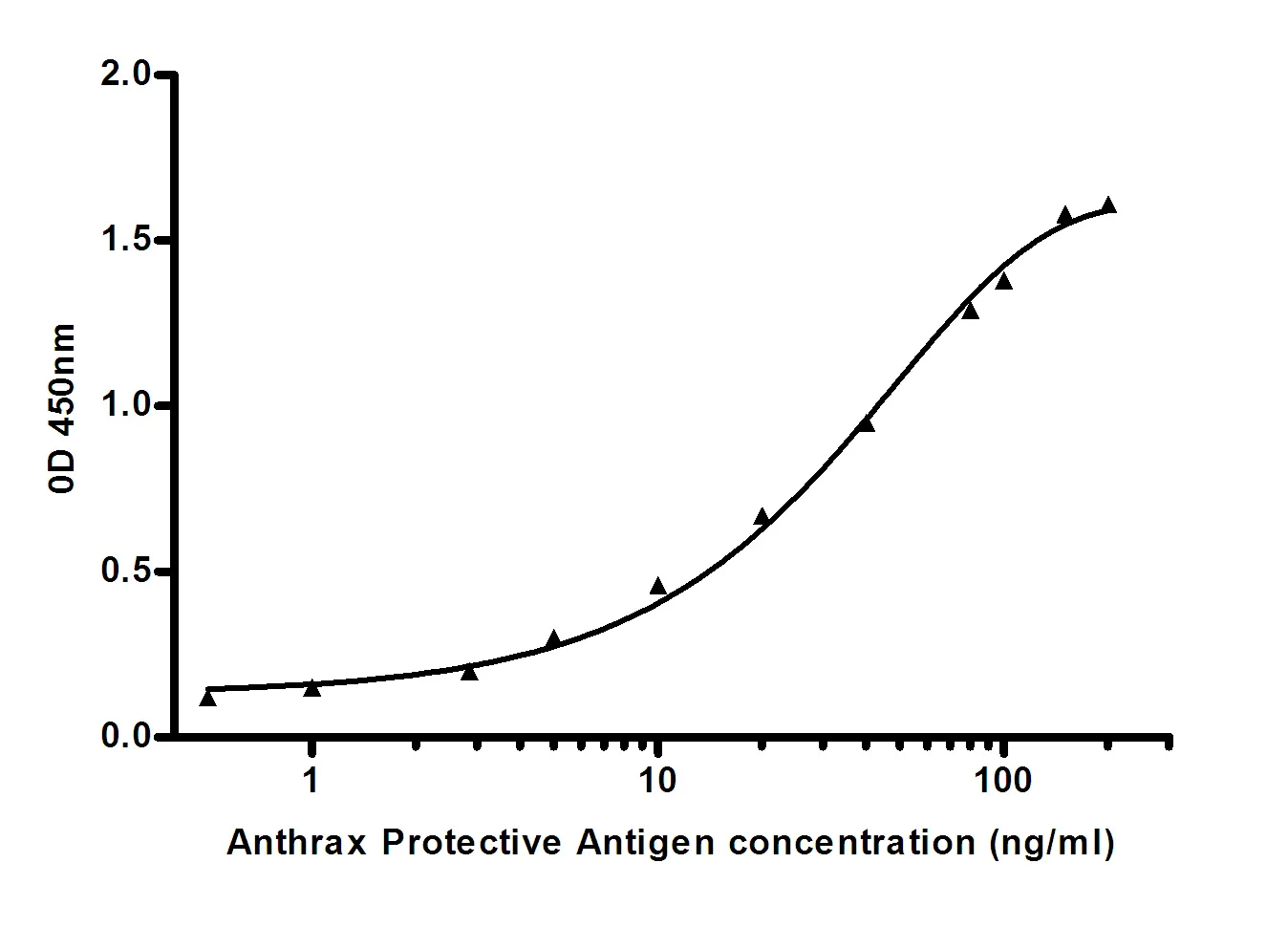
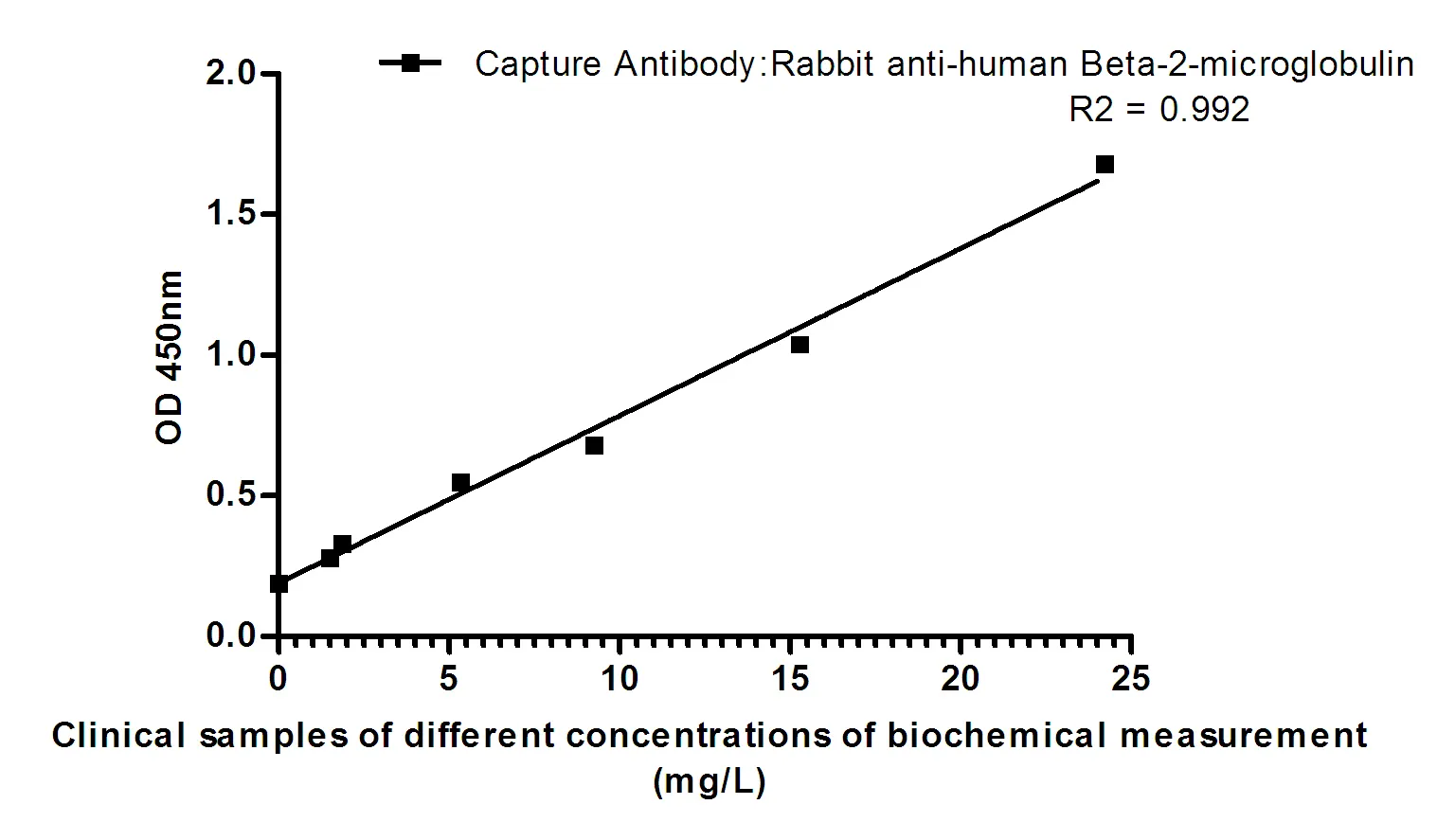
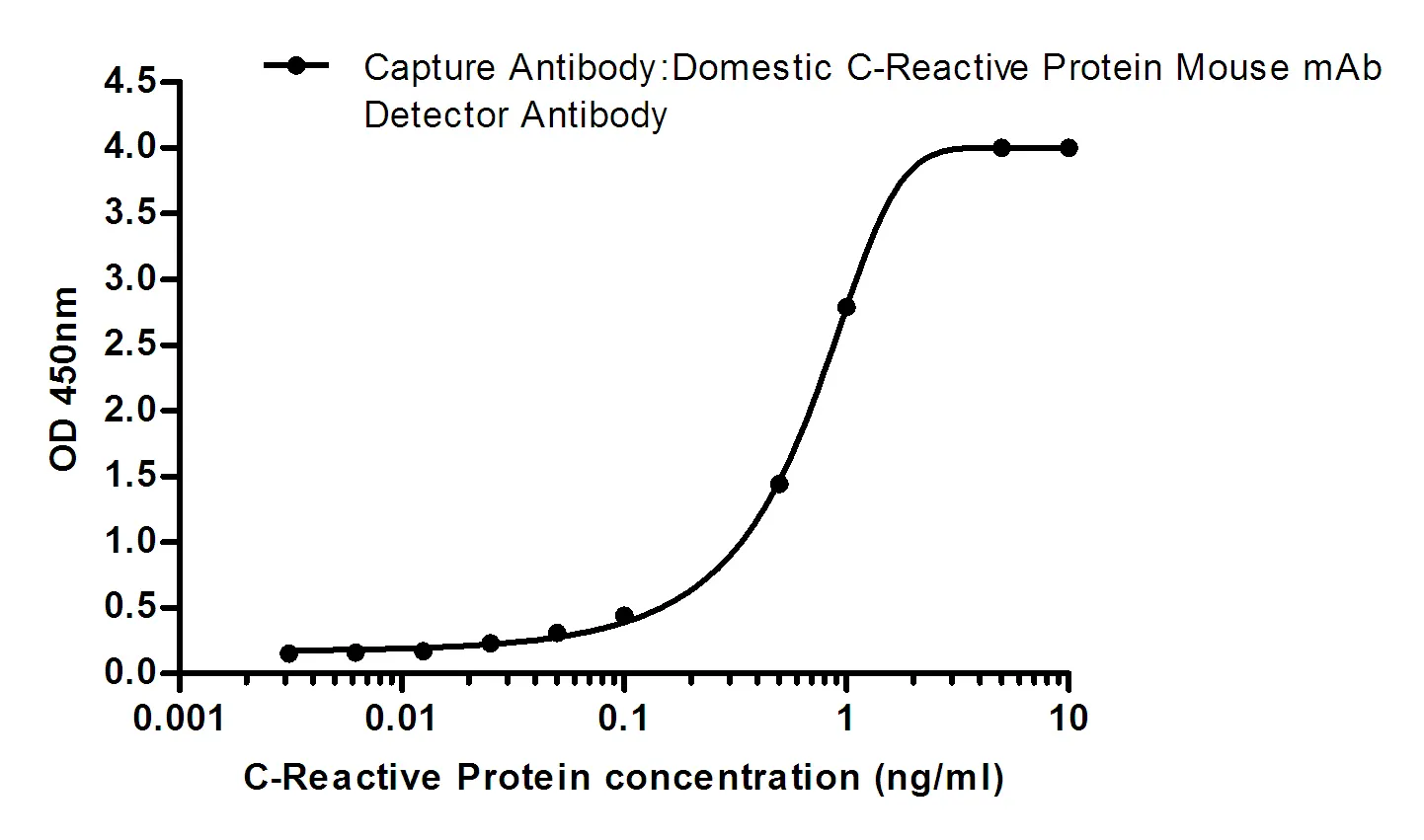
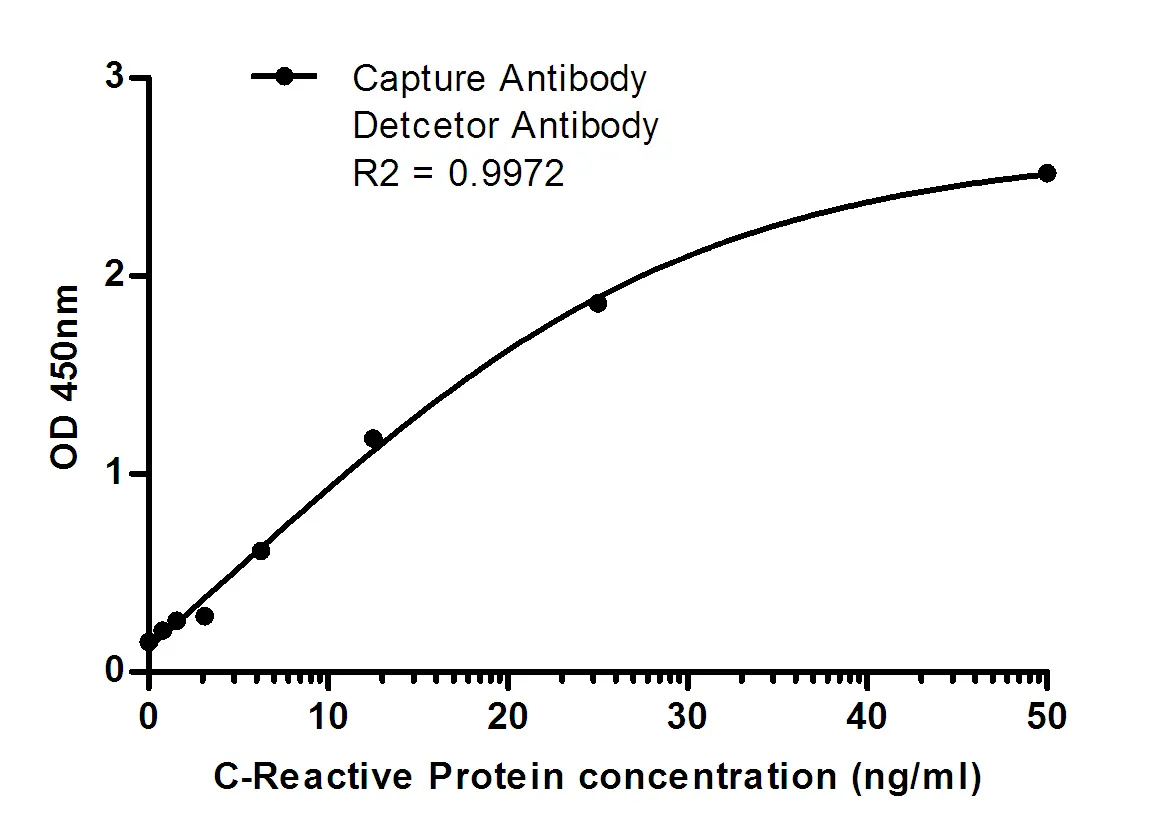
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
This gene encodes a member of the NOTCH family of proteins. Members of this Type I transmembrane protein family share structural characteristics including an extracellular domain consisting of multiple epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats, and an intracellular domain consisting of multiple different domain types. Notch signaling is an evolutionarily conserved intercellular signaling pathway that regulates interactions between physically adjacent cells through binding of Notch family receptors to their cognate ligands. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed in the trans-Golgi network to generate two polypeptide chains that heterodimerize to form the mature cell-surface receptor. This receptor may play a role in vascular, renal and hepatic development. Mutations in this gene may be associated with schizophrenia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed.
Research Area
Notch signaling pathway