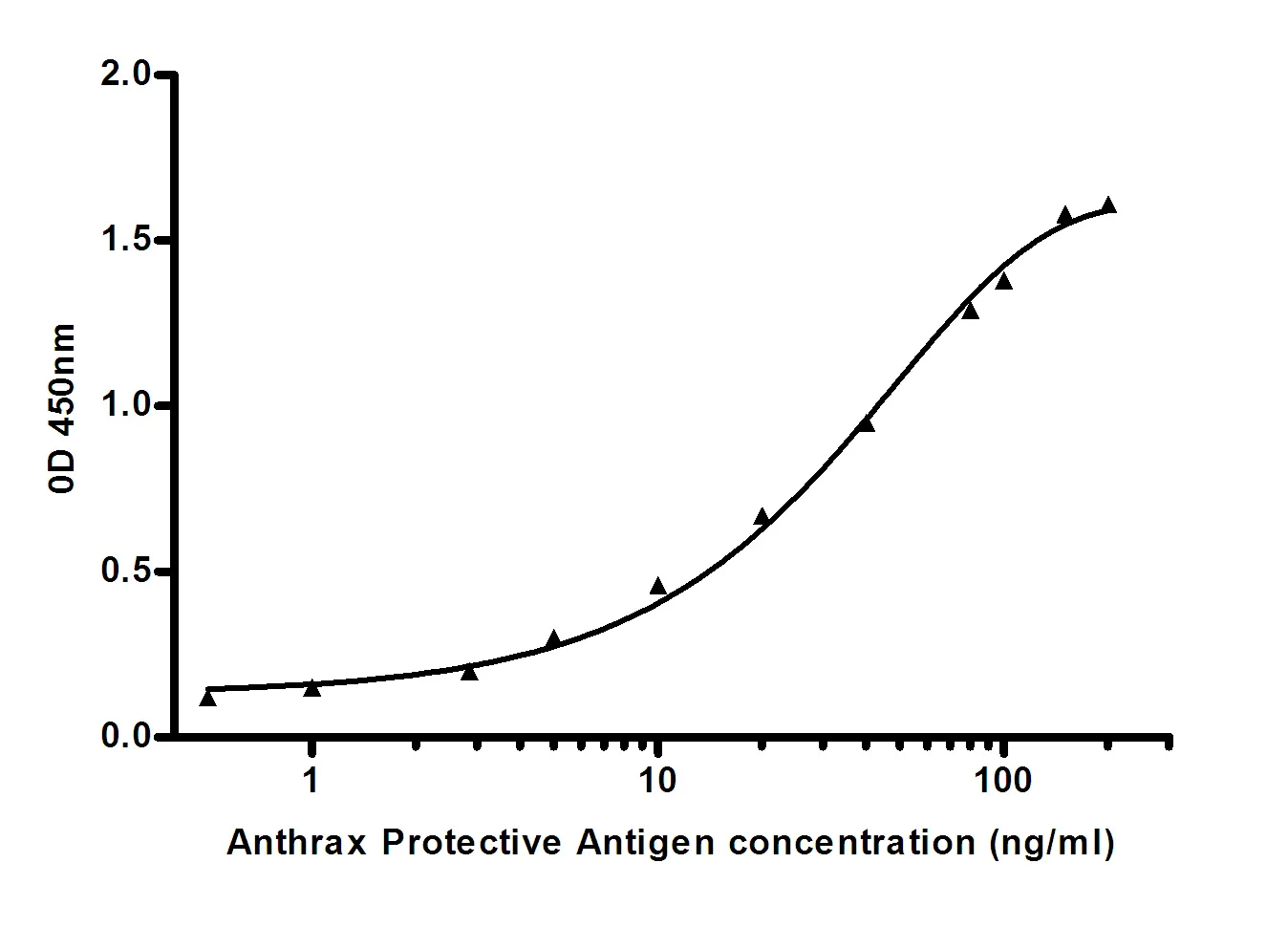
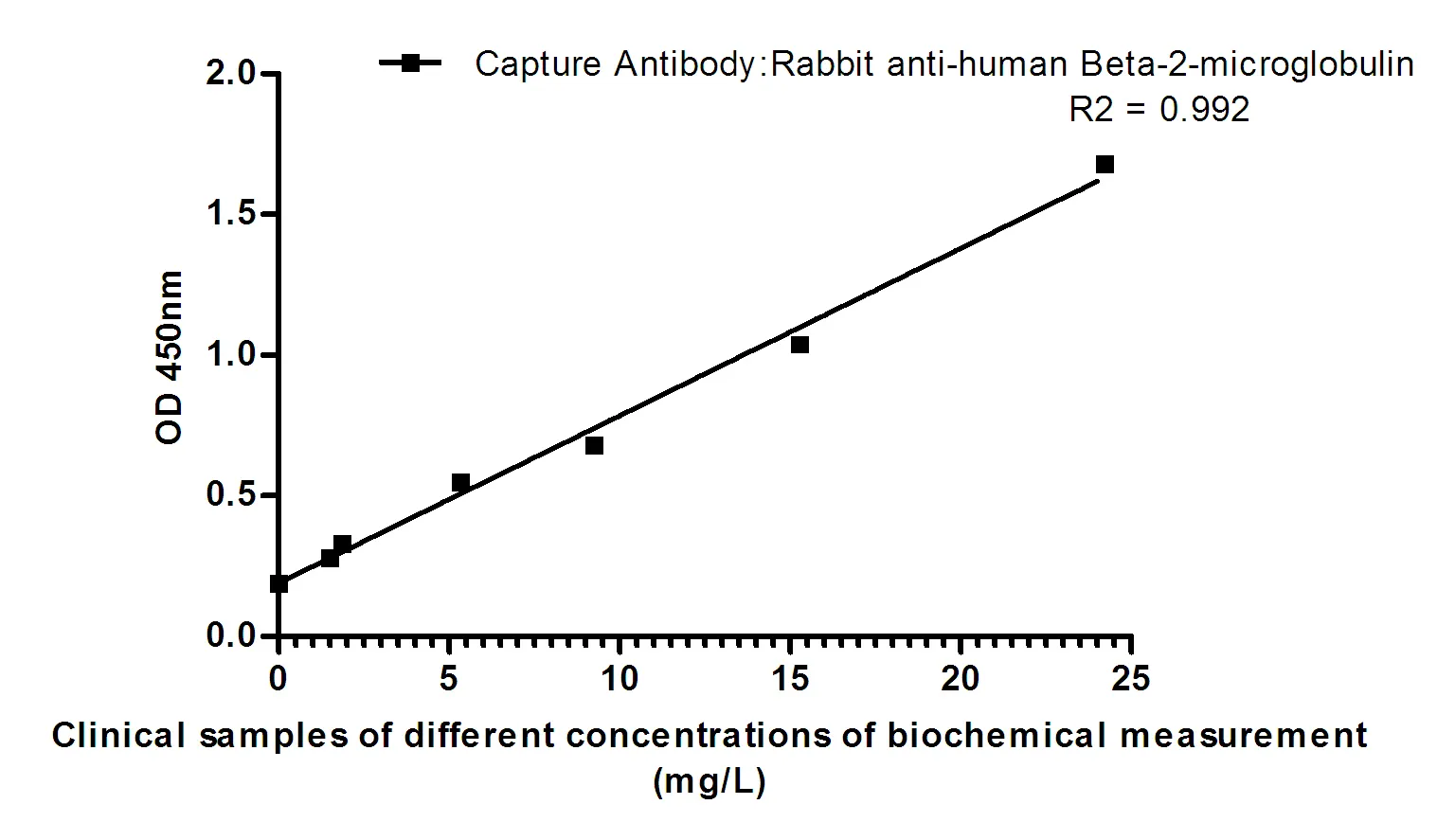
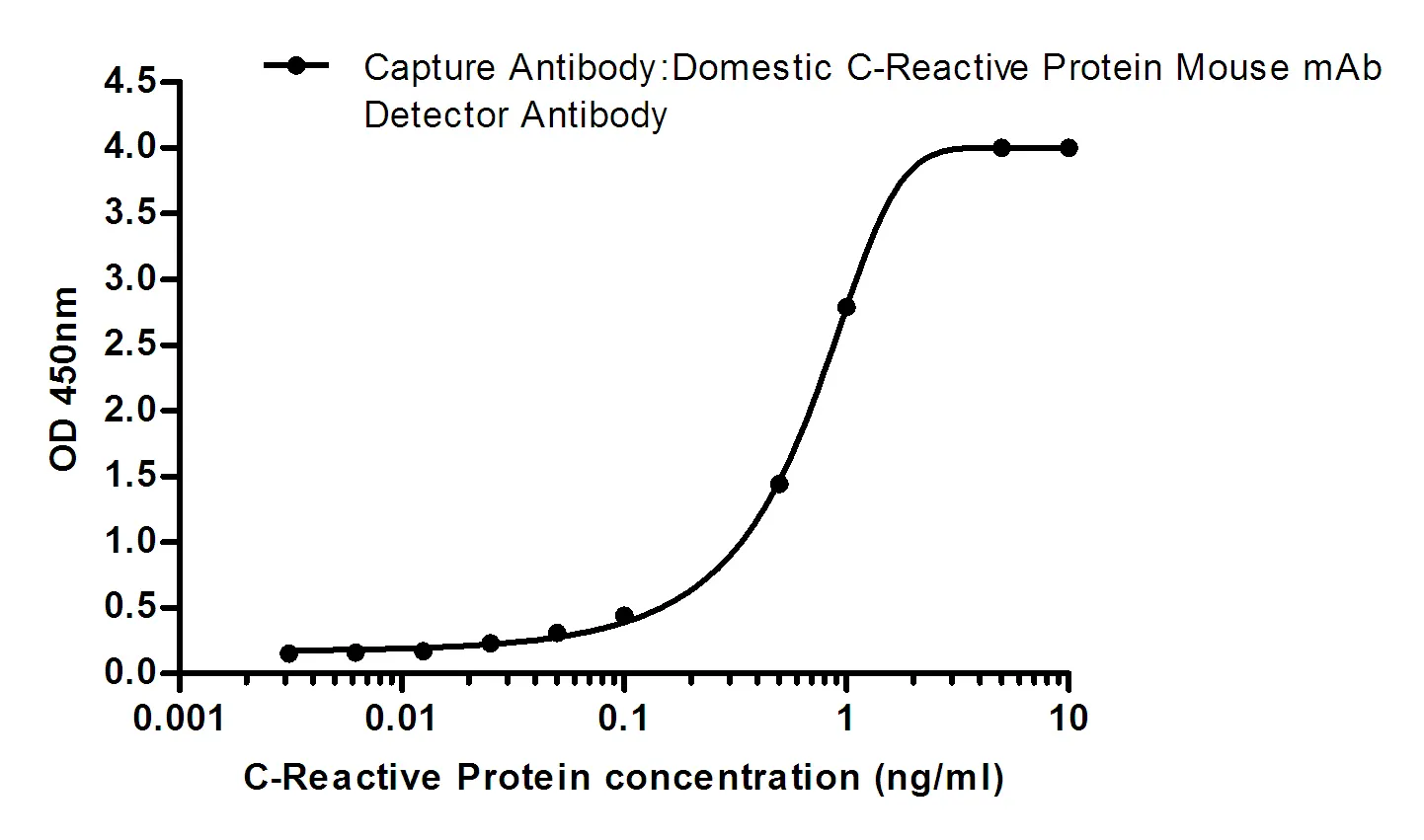
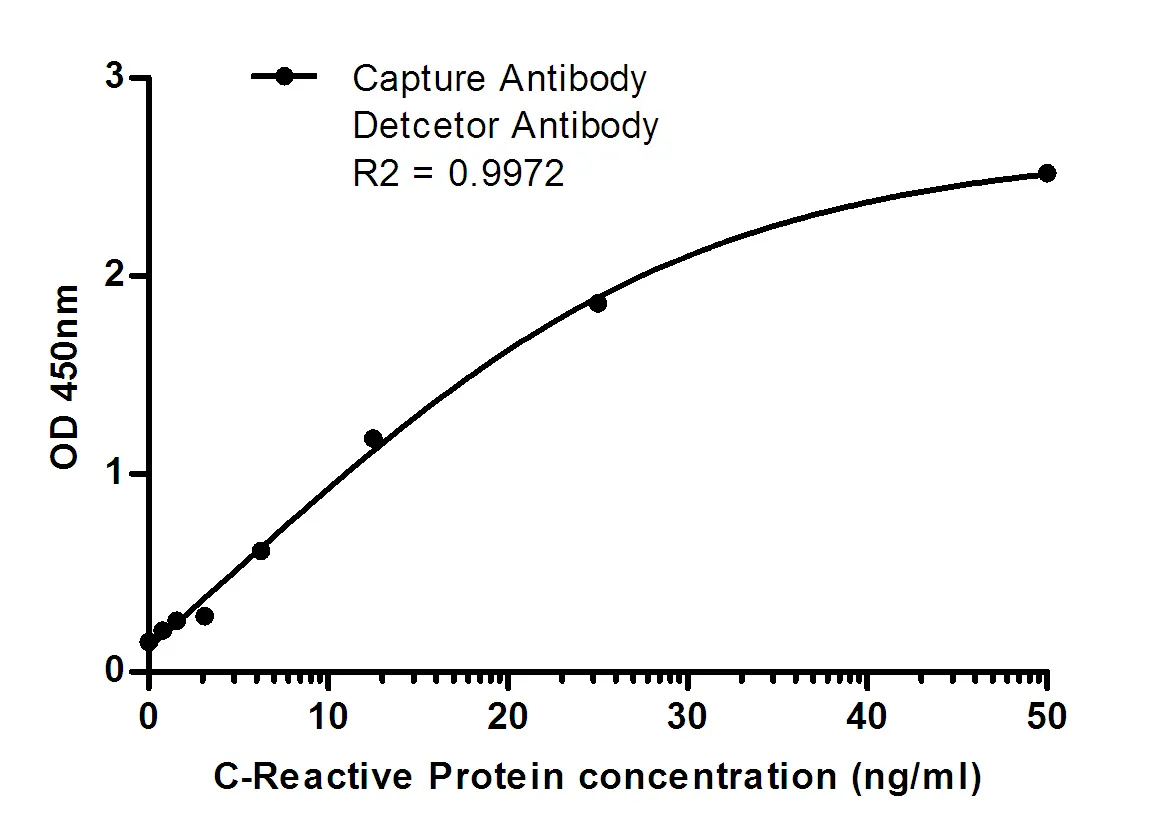
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts downstream of cell surface receptors for growth factors and plays a role in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, microtubule assembly, lamellipodia formation, cell adhesion, cell migration and chemotaxis. Acts downstream of EGFR, KIT, PDGFRA and PDGFRB. Acts downstream of EGFR to promote activation of NF-kappa-B and cell proliferation. May play a role in the regulation of the mitotic cell cycle. Plays a role in the insulin receptor signaling pathway and in activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Acts downstream of the activated FCER1 receptor and plays a role in FCER1 (high affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor)-mediated signaling in mast cells. Plays a role in the regulation of mast cell degranulation. Plays a role in leukocyte recruitment and diapedesis in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Plays a role in synapse organization, trafficking of synaptic vesicles, the generation of excitatory postsynaptic currents and neuron-neuron synaptic transmission. Plays a role in neuronal cell death after brain damage. Phosphorylates CTTN, CTNND1, PTK2/FAK1, GAB1, PECAM1 and PTPN11. May phosphorylate JUP and PTPN1. Can phosphorylate STAT3, but the biological relevance of this depends on cell type and stimulus.
Research Area
Adherens_Junction;