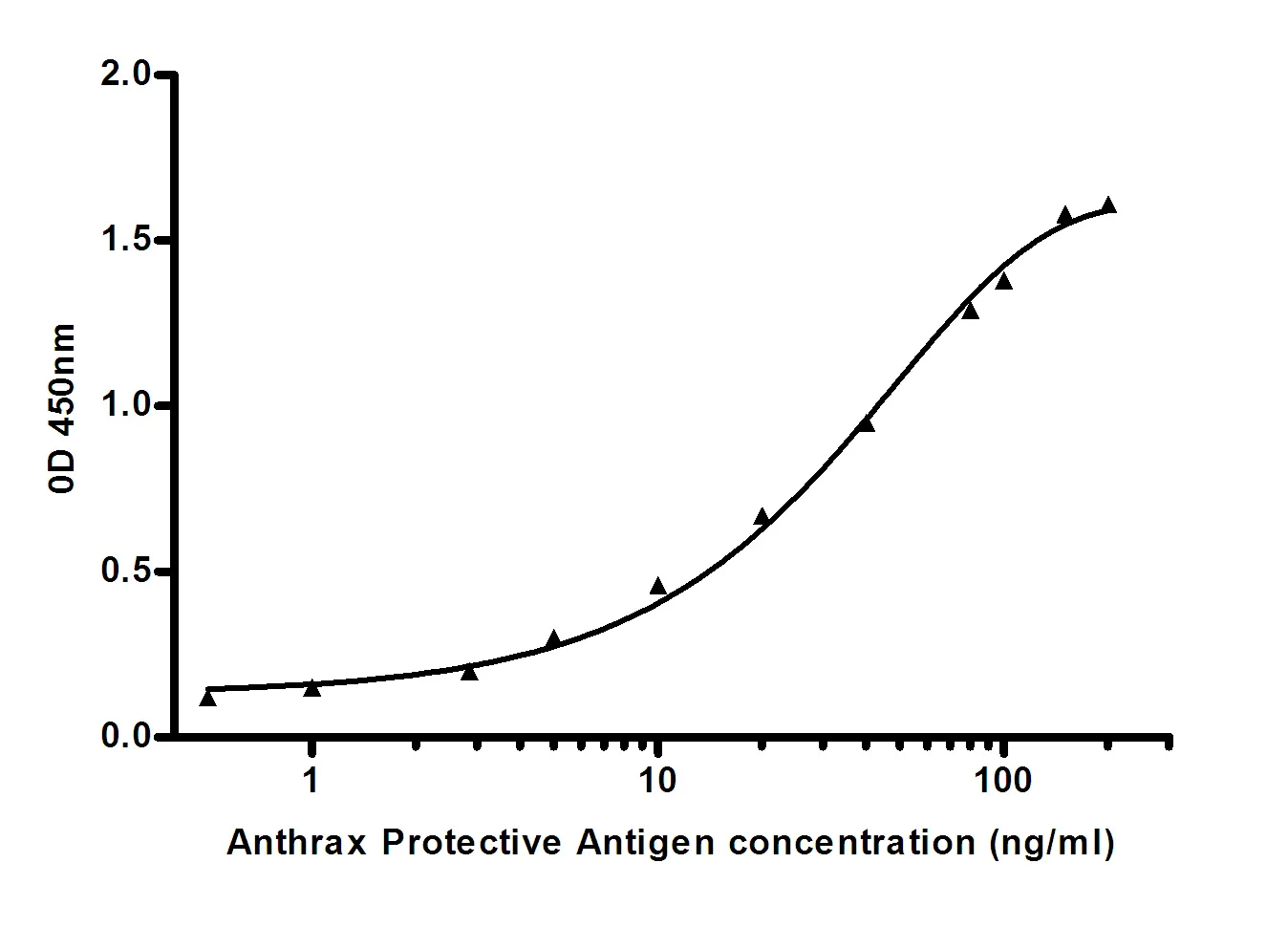
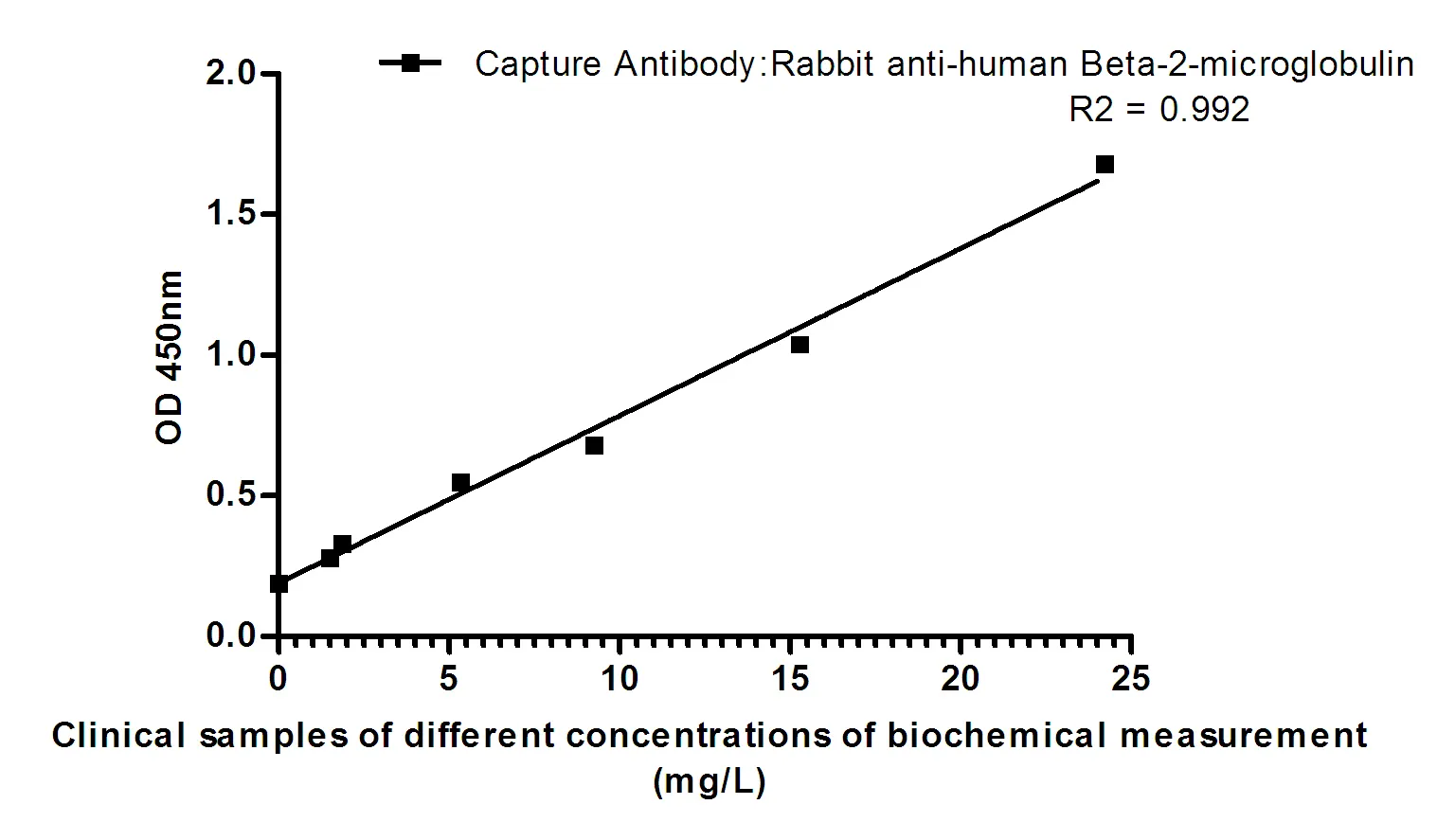
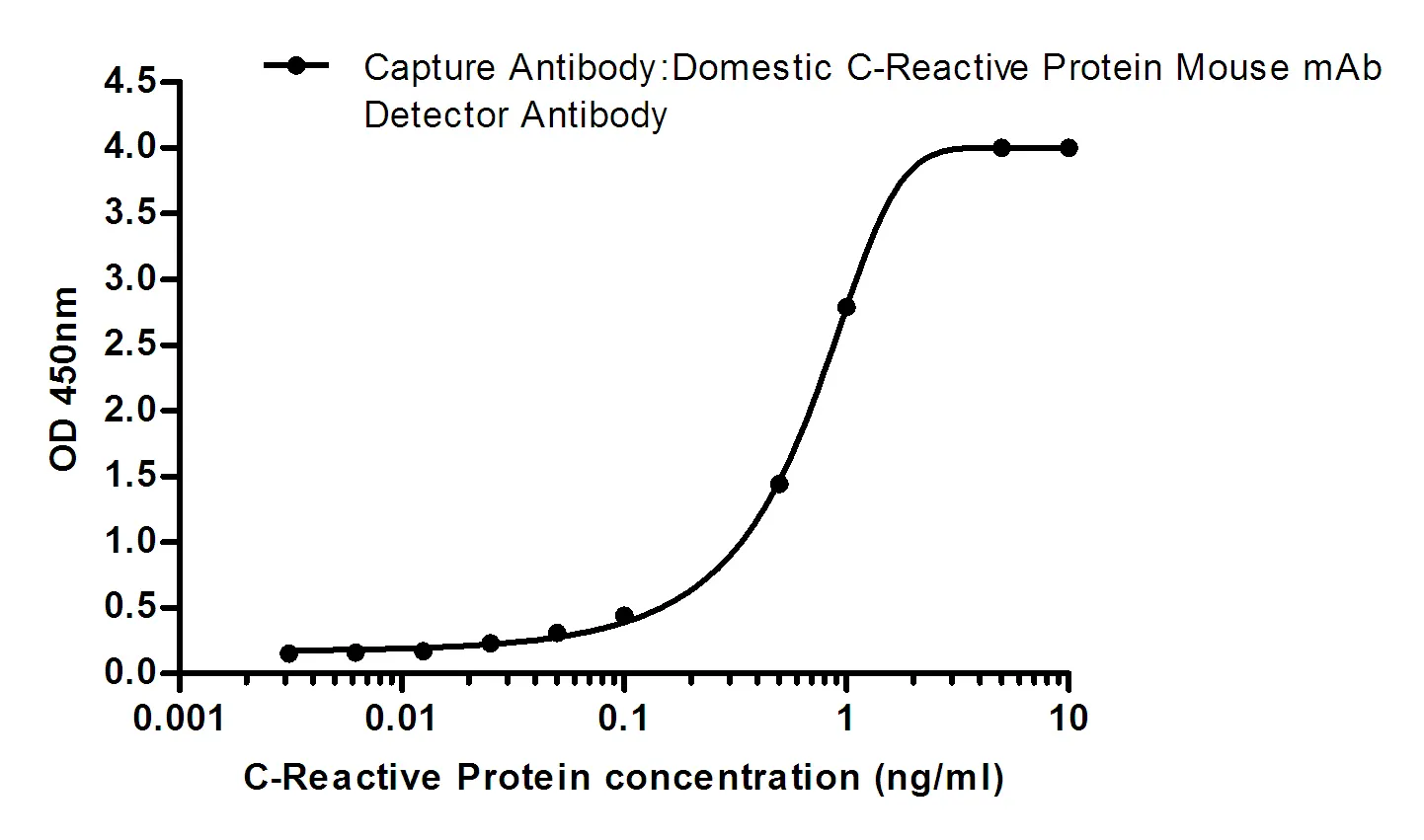
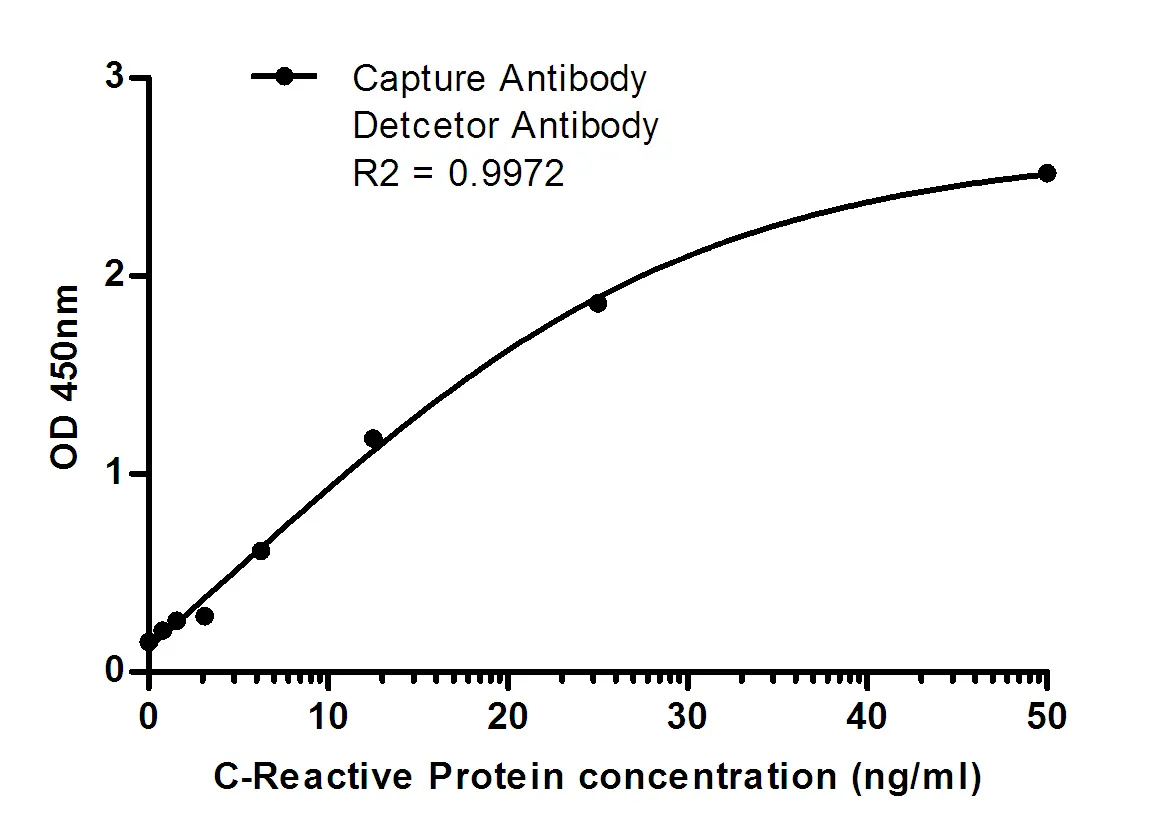
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Acetylcholinesterase hydrolyzes the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions and brain cholinergic synapses, and thus terminates signal transmission. It is also found on the red blood cell membranes, where it constitutes the Yt blood group antigen. Acetylcholinesterase exists in multiple molecular forms which possess similar catalytic properties, but differ in their oligomeric assembly and mode of cell attachment to the cell surface. It is encoded by the single ACHE gene, and the structural diversity in the gene products arises from alternative mRNA splicing, and post-translational associations of catalytic and structural subunits. The major form of acetylcholinesterase found in brain, muscle and other tissues is the hydrophilic species, which forms disulfide-linked oligomers with collagenous, or lipid-containing structural subunits. The other, alternatively spliced form, expressed primarily in the erythroid tissues, differs at the C-terminal end, and contains a cleavable hydrophobic peptide with a GPI-anchor site. It associates with the membranes through the phosphoinositide (PI) moieties added post-translationally. AChE activity may constitute a sensitive biomarker of RBC ageing in vivo, and thus, may be of aid in understanding the effects of transfusion.
Research Area