Summary
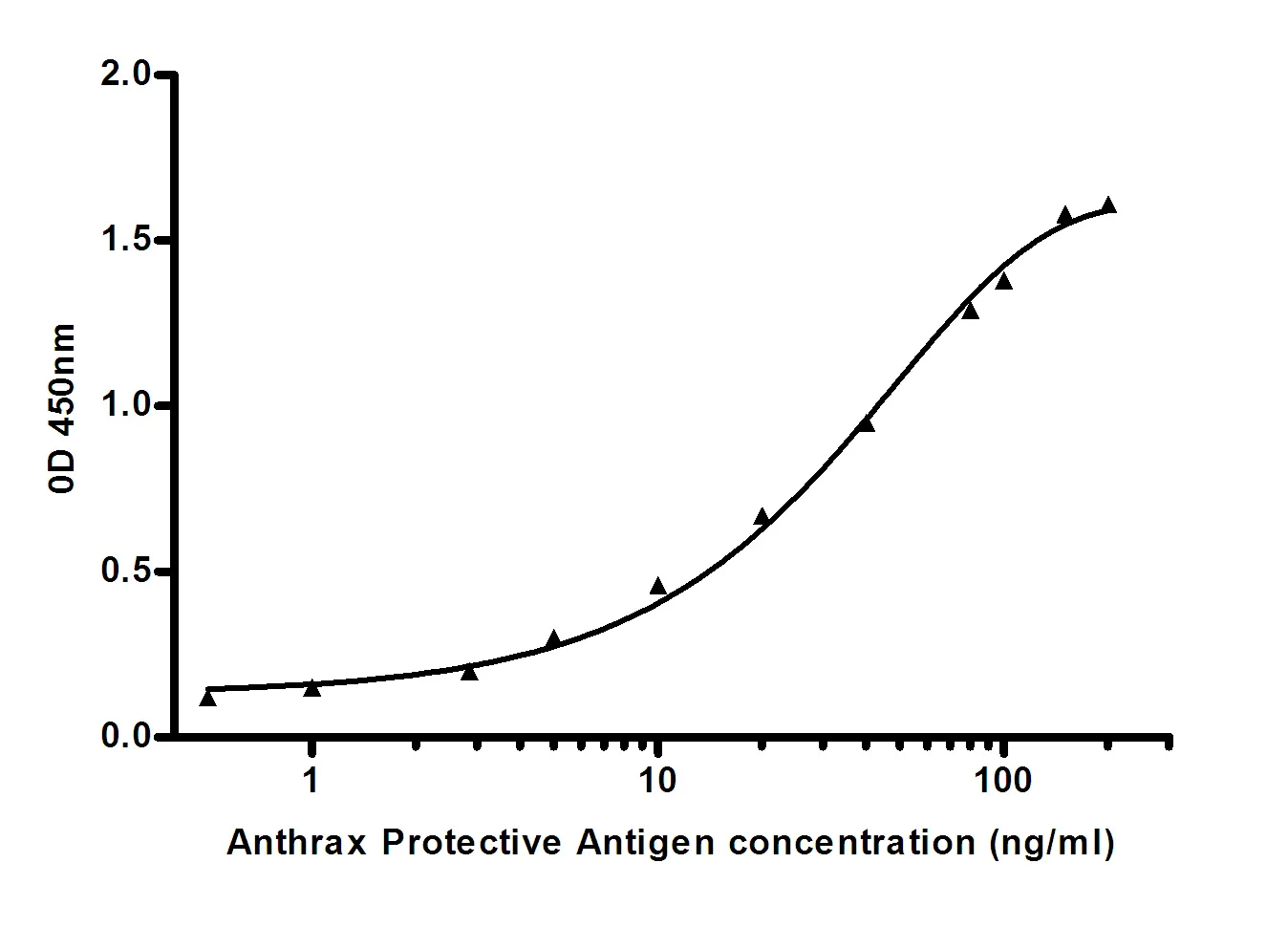
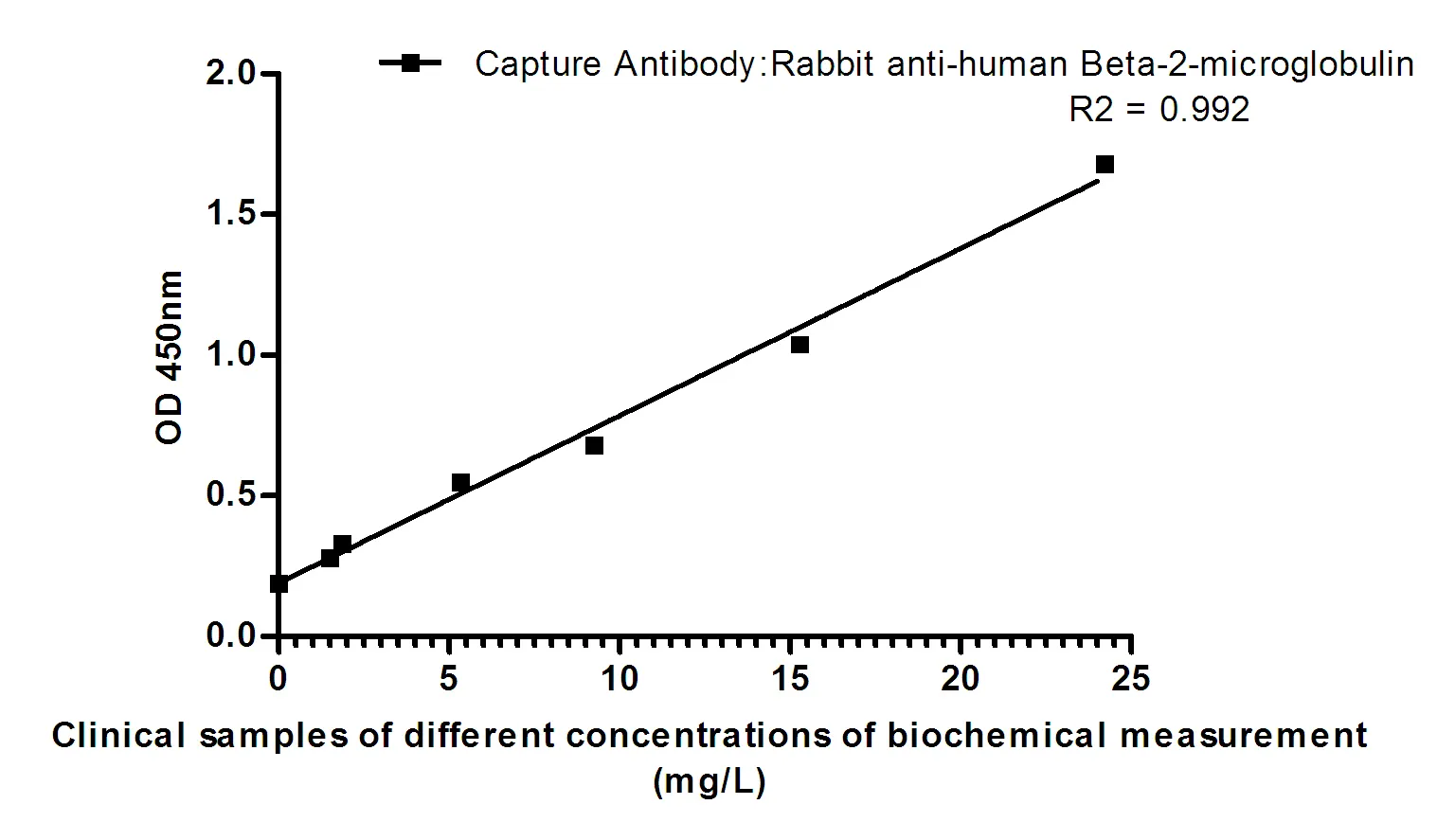
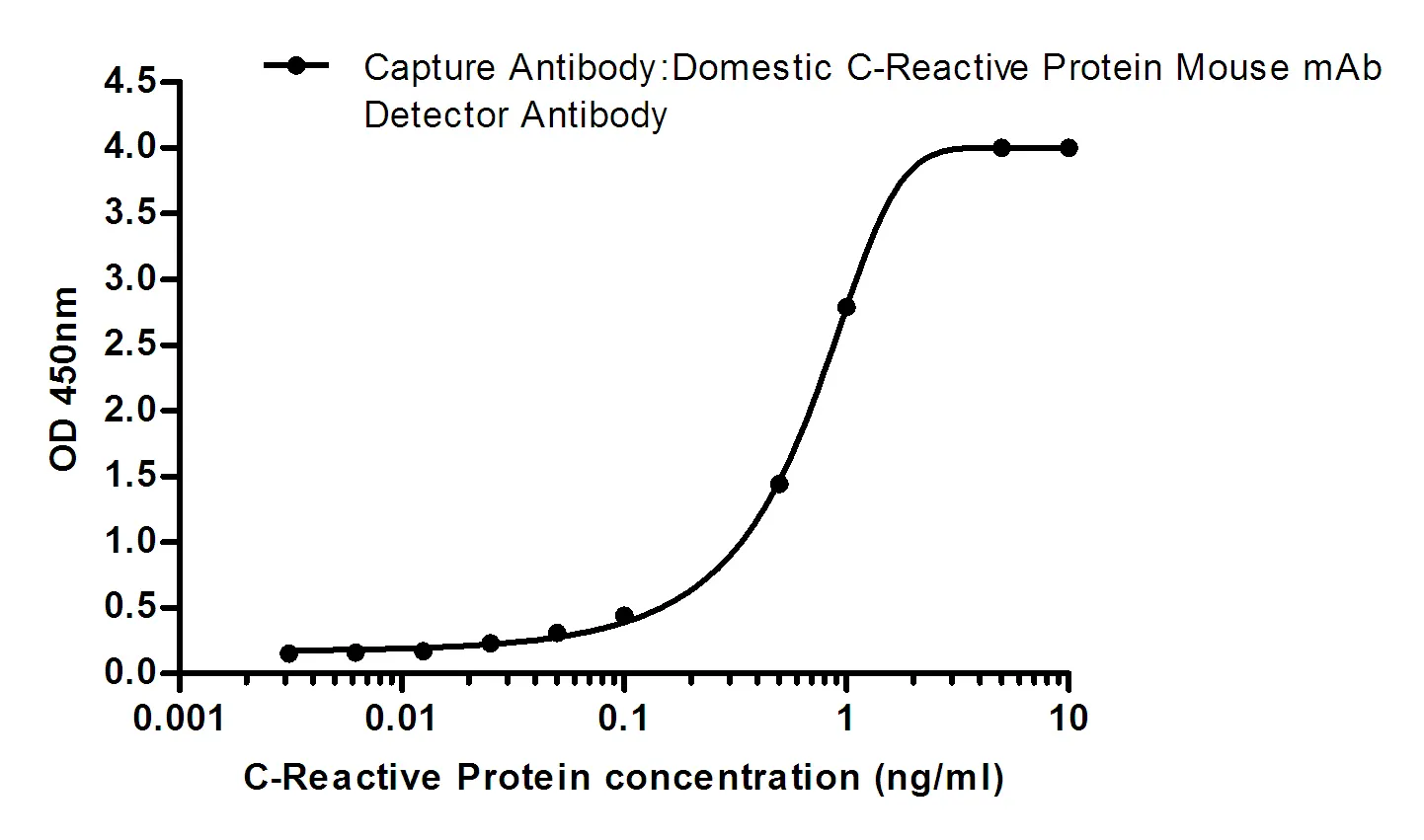
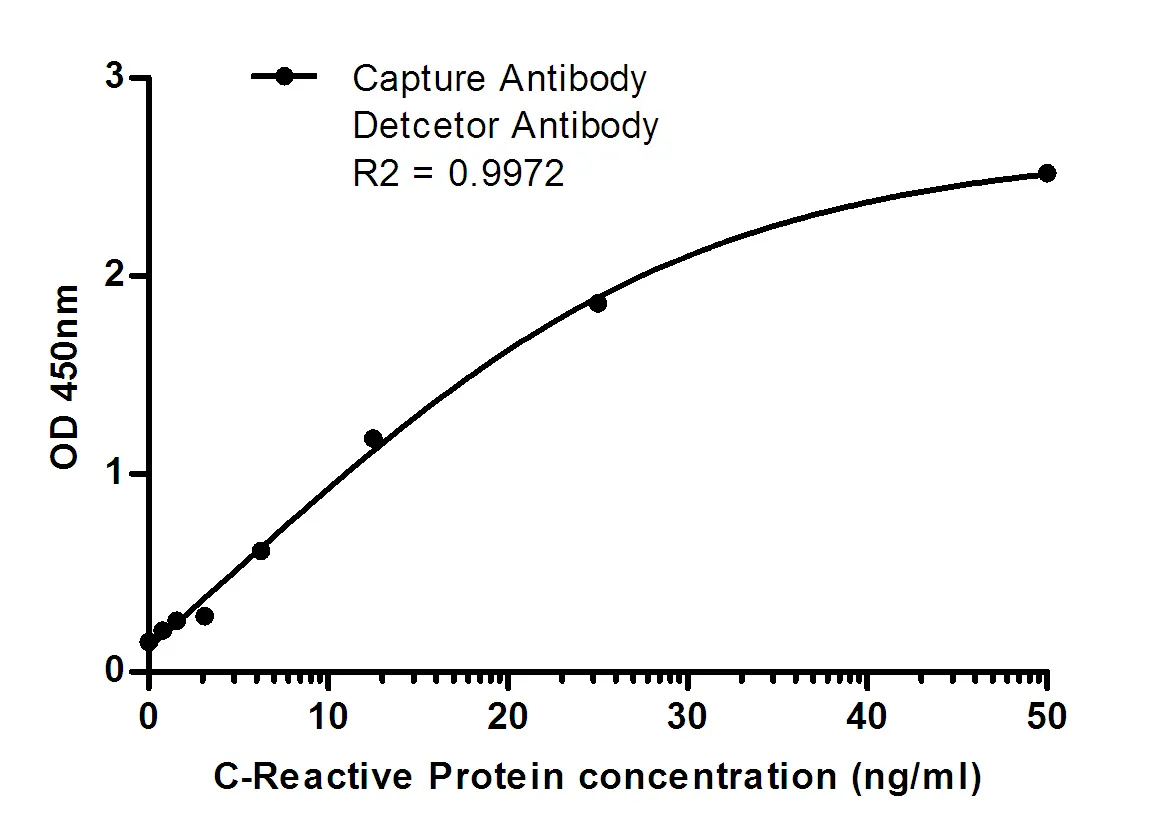
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
The autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxias (ADCA) are a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by progressive degeneration of the cerebellum, brain stem and spinal cord. Clinically, ADCA has been divided into three groups: ADCA types I-III. ADCAI is genetically heterogeneous, with five genetic loci, designated spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6, being assigned to five different chromosomes. ADCAII, which always presents with retinal degeneration (SCA7), and ADCAIII often referred to as the `pure' cerebellar syndrome (SCA5), are most likely homogeneous disorders. Several SCA genes have been cloned and shown to contain CAG repeats in their coding regions. ADCA is caused by the expansion of the CAG repeats, producing an elongated polyglutamine tract in the corresponding protein. The expanded repeats are variable in size and unstable, usually increasing in size when transmitted to successive generations. The function of the ataxins is not known. This locus has been mapped to chromosome 6, and it has been determined that the diseased allele contains 40-83 CAG repeats, compared to 6-39 in the normal allele, and is associated with spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, with one variant encoding multiple distinct proteins, ATXN1 and Alt-ATXN1, due to the use of overlapping alternate reading frames.
Research Area