Summary
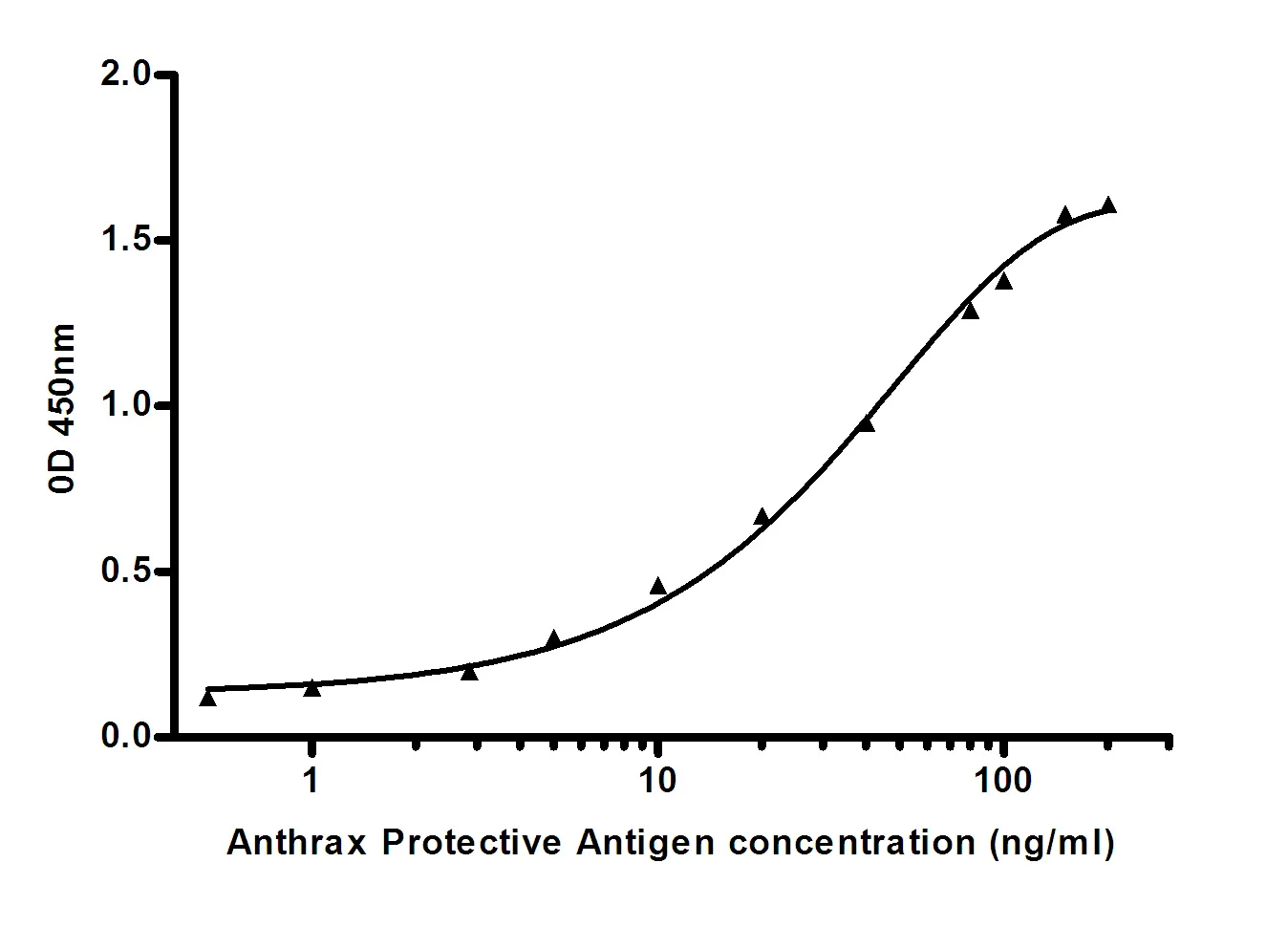
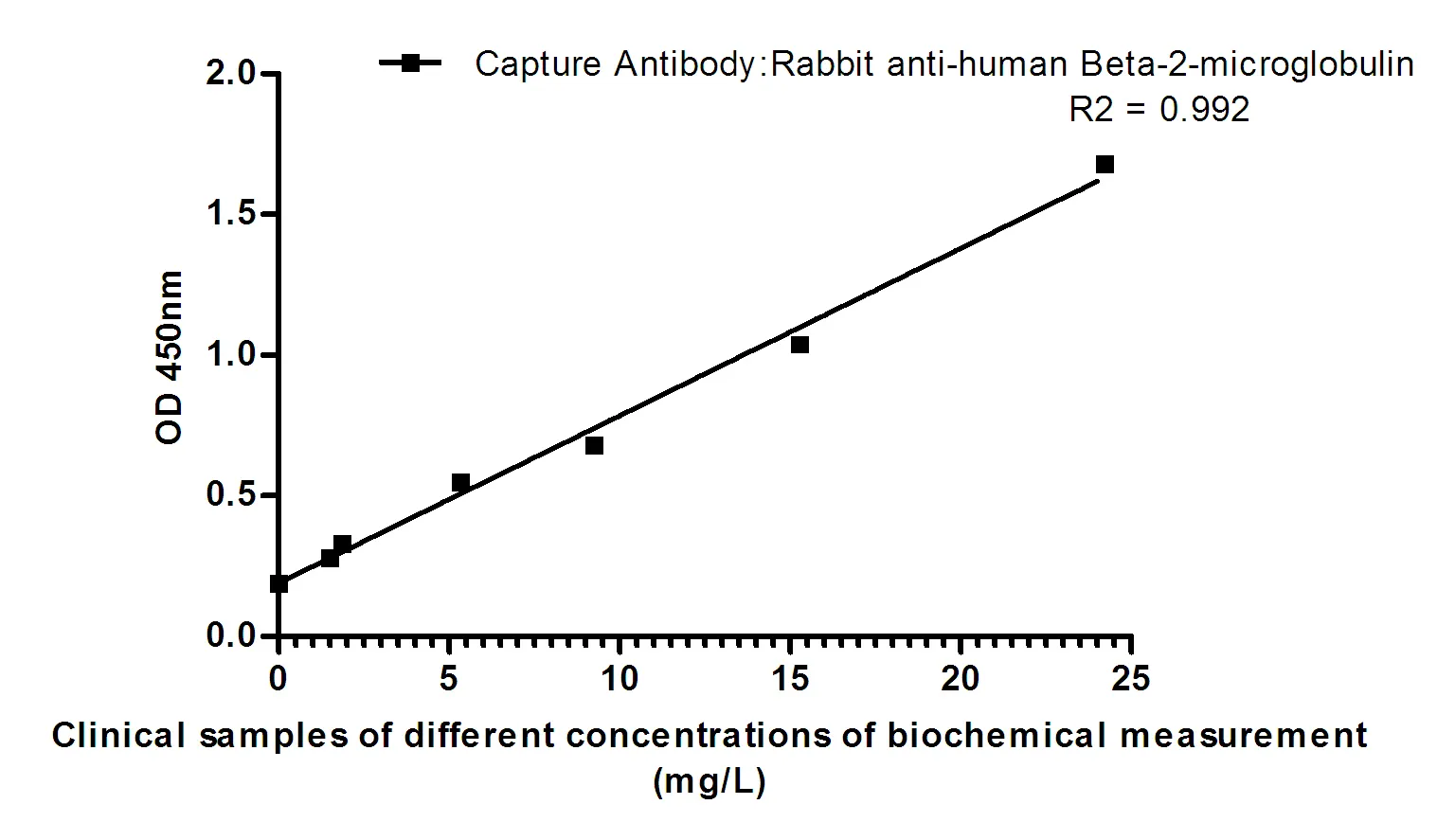
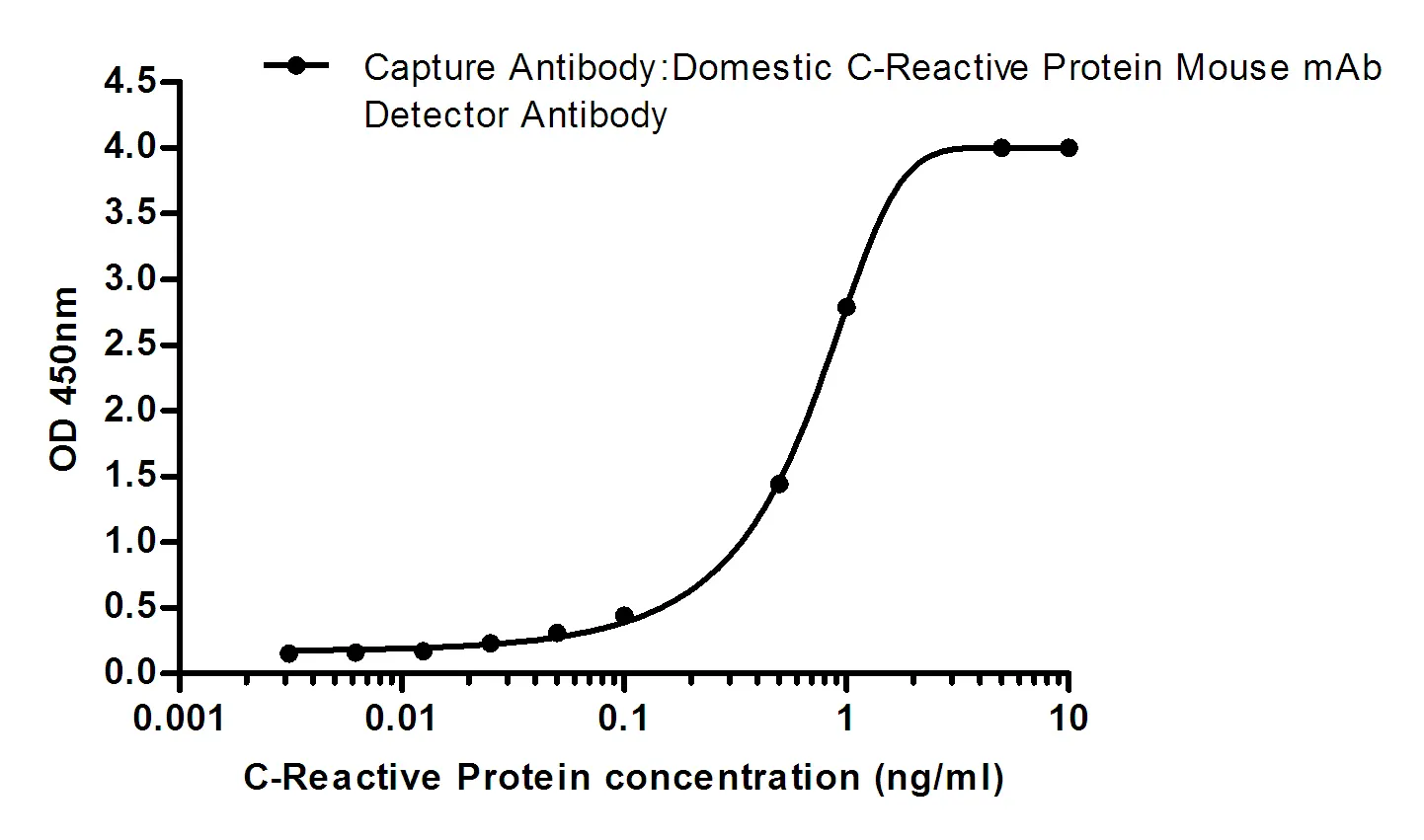
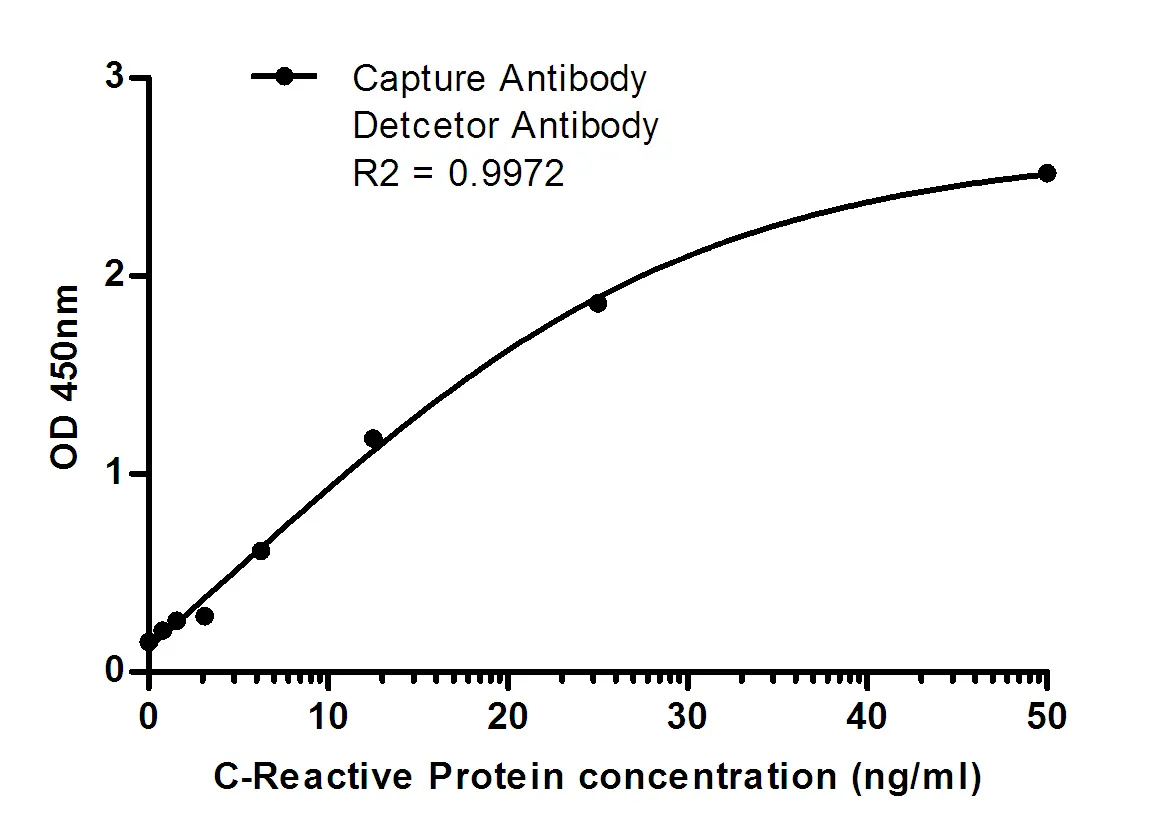
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
This gene encodes a transcriptional coactivator that plays an essential role in regulating gene expression during early development and hematopoiesis. The encoded protein contains multiple conserved functional domains. One of these domains, the SET domain, is responsible for its histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase activity which mediates chromatin modifications associated with epigenetic transcriptional activation. This protein is processed by the enzyme Taspase 1 into two fragments, MLL-C and MLL-N. These fragments reassociate and further assemble into different multiprotein complexes that regulate the transcription of specific target genes, including many of the HOX genes. Multiple chromosomal translocations involving this gene are the cause of certain acute lymphoid leukemias and acute myeloid leukemias. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
Research Area
Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction;