Product Introduction
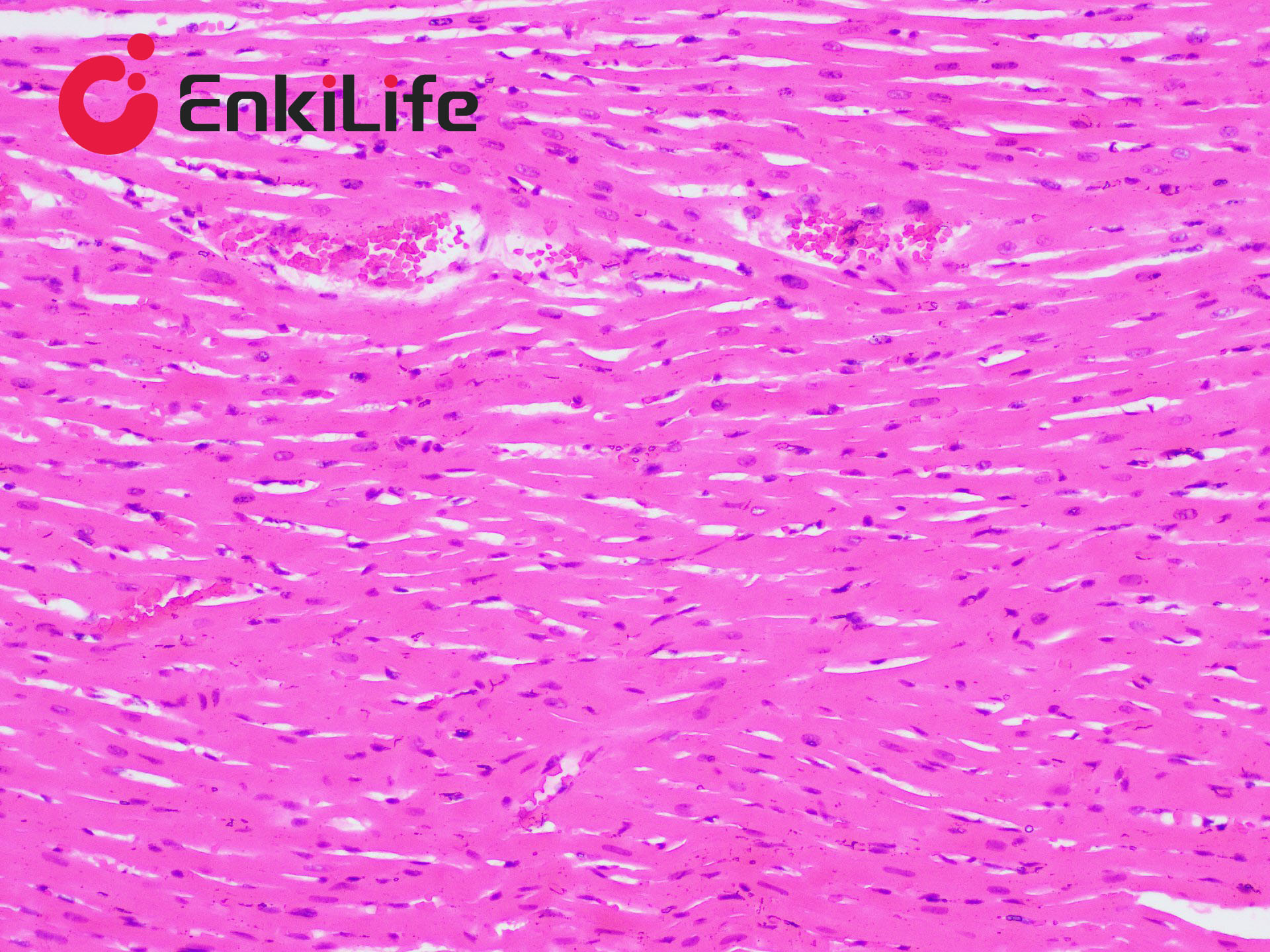
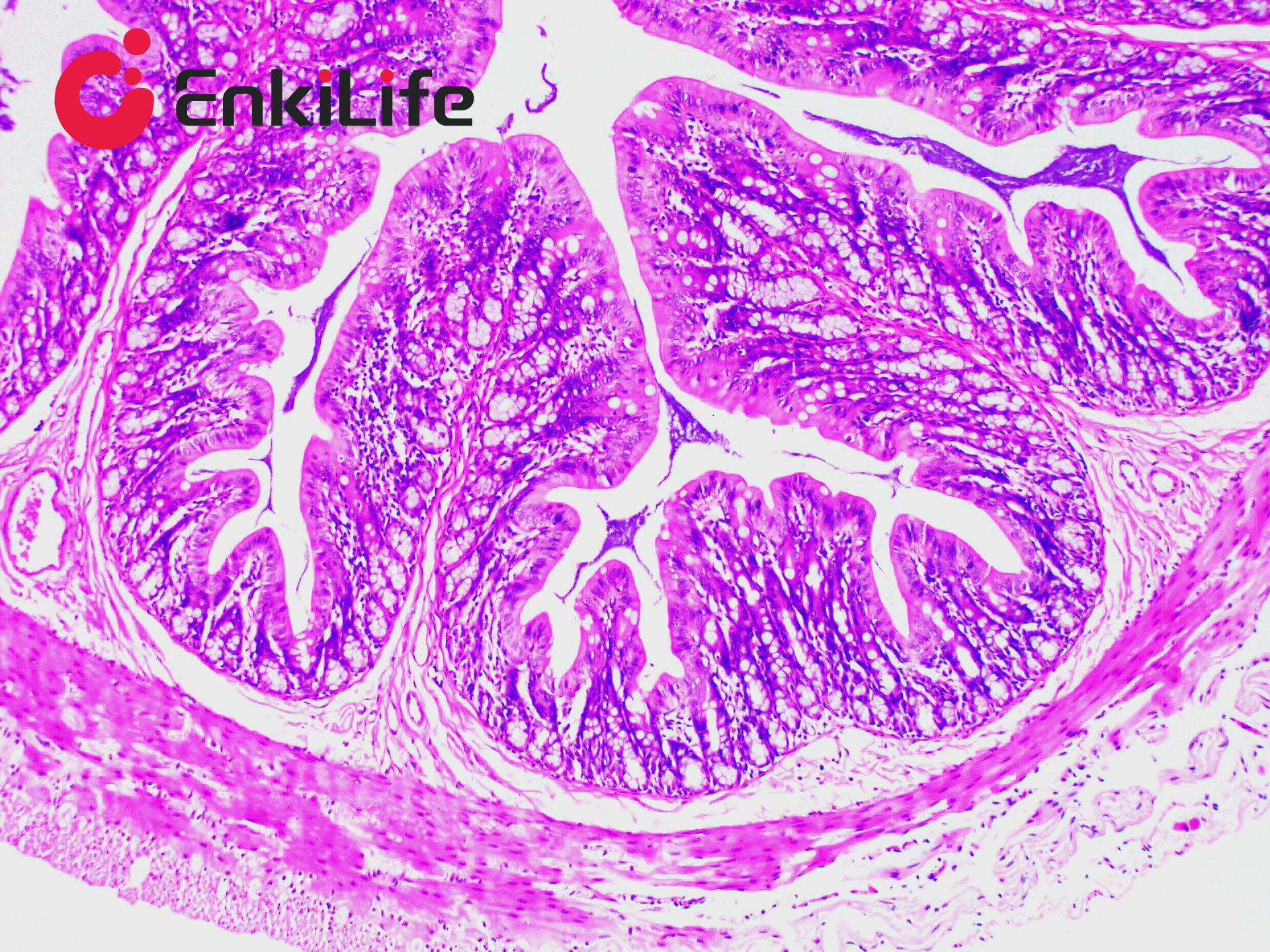
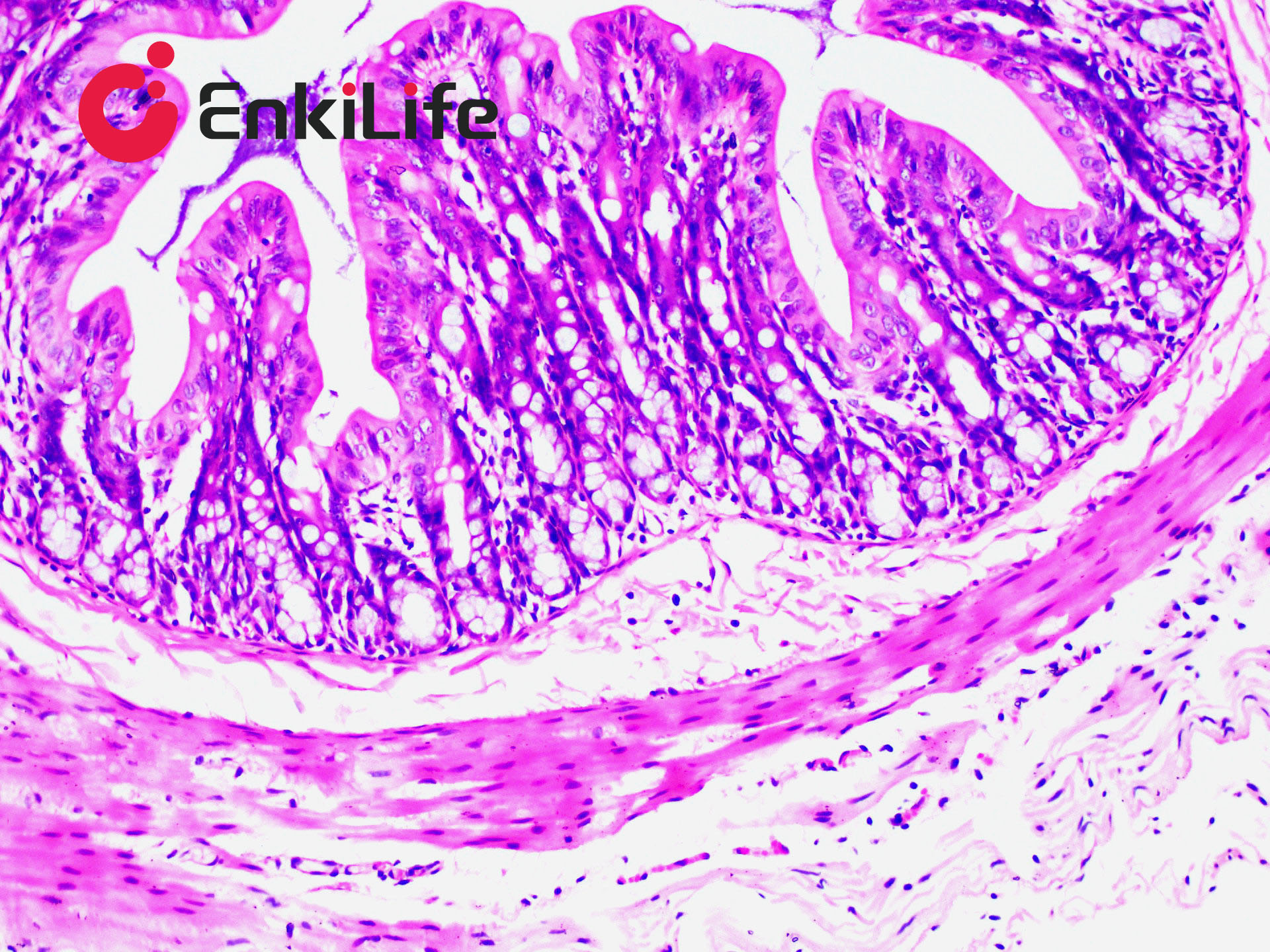
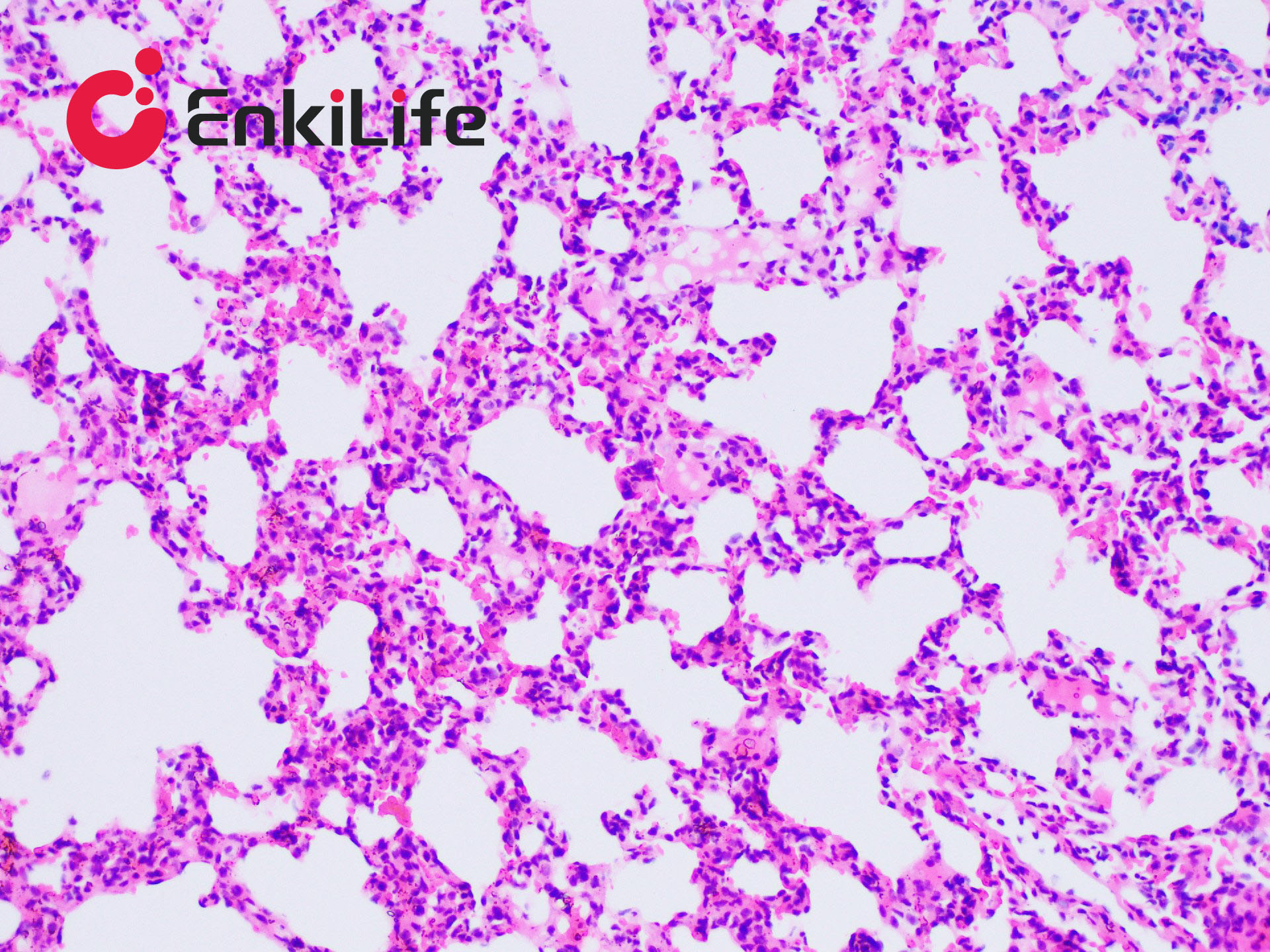
Connective tissue, in a narrow sense, refers to the three types of fibers it contains: collagen fibers, reticular fibers, and elastic fibers. Among them, collagen fibers are the most widely distributed and abundant. Masson trichrome staining, also known as Masson staining, is the most classical method for connective tissue staining and is an authoritative and traditional technique for collagen fiber visualization.
The so-called "trichrome" staining typically refers to staining the nucleus and selectively displaying collagen and muscle fibers. The staining principle is related to the size of anionic dye molecules and tissue permeability: smaller molecules penetrate dense, low-permeability tissues more easily, while larger molecules only enter loosely structured, high-permeability tissues. Since light green or aniline blue have large molecular weights, after Masson staining, muscle fibers appear red, while collagen fibers appear green (light green) or blue (aniline blue). This method is mainly used to distinguish collagen fibers from muscle fibers.
EnkiLife’s Masson Trichrome Staining Solution features: Stable staining; Short differentiation time; Clear and bright colors; Wide application range, suitable for paraffin and frozen sections; Stained sections can be stored for a long time without fading.
Basic Information
Product name | Masson Trichrome Staining Kit |
Sizes | 50 mL, 100 mL |
Storage | RT, keep away from light |
Shipping | RT |
Validity | 12 months |
Product Components
Components | 7x 50mL | 7x 100mL | |
Reagent (A): Weigert Iron Hematoxylin Staining Solution | A1: Weigert Solution A | 25 mL | 50 mL |
A2: Weigert Solution B | 25 mL | 50 mL | |
Mix A1 and A1 in equal parts before use. Do not prepare in advance. | |||
Reagent (B): Acid Ethanol Differentiation Solution | 50 mL | 100 mL | |
Reagent (C): Masson Blue Solution | 50 mL | 100 mL | |
Reagent (D): Ponceau Fuchsin Staining Solution | 50 mL | 100 mL | |
Reagent (E): Weak Acid Solution | 50 mL | 100 mL | |
Reagent (F): Phosphomolybdic Acid Solution | 50 mL | 100 mL | |
Reagent (G): Aniline Blue Staining Solution | 50 mL | 100 mL | |
Notes
1. This staining solution can be used with either drop staining or immersion staining. For small sample numbers, drop staining is recommended.
2. Deparaffinization should be thorough. Fixation plays a key role; different fixatives may extend or shorten staining time.
3. For frozen sections, fix with ether-ethanol mixture or formalin-based fixative for 10 s–3 min, then rinse with water before staining.
4. Mix A1 and A2 in equal parts to prepare Weigert Iron Hematoxylin. It generally loses staining ability after 24 h.
5. Acid ethanol differentiation time should be adjusted based on section thickness, tissue type, and tissue age.
6. This method uses Weigert Iron Hematoxylin to stain nuclei. Harris Hematoxylin may also be used, but the nuclear color may not be as vivid. The main purpose of this staining is to distinguish collagen fibers from muscle fibers; bright and clear contrast is sufficient, and nuclear staining is optional.
7. Hematoxylin (blue) stains nuclei, Ponceau acid fuchsin (red) stains muscle fibers, and aniline blue (blue) or fast green (green) stains collagen fibers. Using fast green enables trichrome staining; using aniline blue results in two-color staining.
8. Weak acid solution enhances color clarity and brightness. If used in large quantities, it can be replaced with 0.1–0.3% acetic acid solution.
9. Phosphomolybdic acid differentiates collagen fibers stained red to colorless or light red, while muscle and fibrin remain red. It also acts as a mordant for collagen, enhancing binding with large-molecule dyes. Differentiation time is usually 1–2 min, depending on staining intensity.
10. Masson blue solution can be replaced with Scott tap water substitute or 0.1–1% lithium carbonate aqueous solution.
11. For your safety and health, wear a lab coat and disposable gloves during operation.